Sample Paper Class 10 Social science Term 2 Set A
Please refer to Sample Paper Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Set A with solutions provided below. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science as per the latest paper pattern and examination guidelines for Standard 10 Social Science issued by CBSE for the current academic year. The below provided Sample Guess paper will help you to practice and understand what type of questions can be expected in the Class 10 Social Science exam.
CBSE Sample Paper Class 10 Social Science for Term 2 Set A
SECTION – A
1. Discuss the various stages of the Non-Cooperation Movement launched by Mahatma Gandhi.
Answer : Gandhiji proposed that the movement should unfold in stages:
1st stage – Surrender of titles that the government awarded.
2nd stage – Boycott of civil services, army, police, courts and legislative councils, schools and foreign goods.
3rd stage – Then, in case the government used repression, a full civil disobedience campaign would be launched.
2. Describe the rural roads in India.
Answer : (i) Rural roads link rural areas and villages with important towns.
(ii) These roads received special impetus under the
Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana.
(iii) Special provisions are made so that every village in the country is linked to a major town in the country by an all season motorable road.
3. What are recognised political parties?
Answer : In India, Election Commission gives special facilities to large and established parties. They are given a unique symbol and official candidates can use the symbol in elections. Those parties which are given this type of privileges and facilities and are recognized by Election Commission are known as recognized political parties.
4. Why do banks or lenders demand collateral against loans?
Answer : Banks or lenders ask for collaterals for the safety of their capital. If the borrower stops making the promised loan repayments, the lender can seize the collateral to recover its money. Thus collateral offer security to the lender against default.
5. Explain with examples the interdependence of agriculture and industries.
Answer : The interdependence of agriculture and industries is based on many things like adequate rainfall and good crops.
Some of the examples are when the rains fail the crops fail, the industries suffer and we have losses in our business as the purchasing power of the farmers fall.
If the cotton crops fail the clothing industries suffer and the industries suffer.
If the poultry farms does not produce enough eggs the bakery industries which use egg as their important ingredient suffers. Thus we see that industry and agriculture is inter related.
SECTION – B
6. “Self Help Groups’ help borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral.” Examine the statement.
OR
Review any three merits and any two demerits of ‘Formal sector of credit’ in India.
Answer : Self help groups (SHG) have helped borrowers to borrow money without collateral in the following ways:
(i) Self help groups have organized rural poor more so women in pooling their money and in extending loans to its members.
(ii) SHG charge less rate of interest as compared to other forms of banking money lenders.
(iii) These groups gradually can seek loans from bank so as to create employment opportunities for its members.
(iv) Banks have been extending loans to these groups which facilitates their functions.
(v) These SHG have emerged as building blocks of the rural poor.
OR
Banks and cooperatives are the formal sources of credit.
Merits :
(i) These institutions are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India. Their rates of interest for loans are monitored. The rates and terms are fixed.
(ii) There is no exploitation by the lenders.
(iii) Everyone can take a loan that includes big businessmen as well as the small cultivators or borrowers.
(iv) The cost of borrowing is usually less.
Demerits :
(i) The procedure to get the loan is time consuming.
(ii) They require collateral security and follow cumbersome paperwork.
7. How could Non-Cooperation become a movement? Give your opinion.
Answer : Non-Cooperation became a movement:
(i) It was the view of Gandhiji that the British rule was set in India with the cooperation of Indians.
(ii) If Indians refused cooperation, British rule in India would collapse within a year and Swaraj would come.
(iii) Gandhiji proposed that the movement should unfold in stages.
(iv) In case the government used repression, a full civil disobedience campaign would be launched.
(v) Mahatma Gandhi and Shaukat Ali toured extensively, mobilising popular support of the movement.
8. “Nearly every one of the state parties wants to get an opportunity to be a part of one or the other national level coalition.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : State parties seeking national level coalition : Before general election of 2014, in three general elections no one national party was able to secure a majority on its own in Lok Sabha. Thus, the national parties were compelled to form alliances with state or regional parties. Since 1996, nearly everyone of the state parties has got an opportunity to be a part of one or the other national level coalition government. This has contributed to the strengthening of federalism and democracy.
SECTION – C
9. What is democracy? What are its various characteristics?
OR
Is it possible for democracy to do economic development, secure the people and maintain the dignity of the people?
Answer : Democracy is a form of government in which the people are supposed to govern. In it the representatives of the people are elected by the voters on the basis of universal adult franchise. It believes in the concepts like liberty, equality and fraternity and these are its functional bases. In it there should be maximum scope for individual and collective development of society and personality. It has the following characteristics :
(i) Rule of the People : Administration in democracy is being directly or indirectly run by the people.
(ii) Interest of the People : In democracy, administration is being run in the interest of the people and interests of the weaker sections are properly cared by the government.
(iii) Principle of Equality : The basic principle of democracy is the principle of equality. In democracy every person is considered as equal. No discrimination is being done on the basis of birth, education, wealth, etc. All the citizens are given equal political rights. Every person has been given the right to vote through universal adult franchise.
(iv) Rule of Majority : Democracy is the rule of majority. Every decision in democracy is being taken with majority. That party forms the government which gets majority in elections. All the decisions are being taken with majority.
OR
Yes, it is possible for democracy to do all the things. We can take examples of Indian democracy which is developing day by day. Five year plans are trying to do development in the country. We can see a lot of development in the fields of agriculture, industries, trade, transport, education, communication, etc. Indian economy is growing at the speed of around
9% per year which very few other economies are achieving. We are developing even after this much of population.
Our government is trying very hard to give security to its people. It has many types of forces like police, military, CRPF, BSF, ITBP, etc. which are working throughout to maintain security of the people. They are facing smugglers, terrorists, anti-social elements and they are doing so with treat courage. They are saving and protecting entire country from the intruders. In this way democracy saves its citizens.
Democracy also tries to give dignity to the life of the people. All the discriminations have been legally abolished. Even untouchability has come to an end. People are given food facilities to live a better life. If any one tries to take away the dignity of any one then he can go to court to save himself from the humiliation. Women are given special care so that their dignity could be maintained. In this way democracy leads to maintenance of dignity of the people.
10. What is globalisation? Describe the role of Multinational Corporations (MNCs) in promoting globalisation process.
OR
Describe the contribution of technology in promoting the process of globalisation.
Answer : Globalisation means integration of the domestic economy with the world economy through trade, capital and technology flows. MNC’s play an important role in the globalisation process. They compete with the local producers thus integrating the markets. The role of MNCs in the process of globalisation can be understood through the following five examples:
(i) MNCs have led to the availability of products from all over the world in any country. For example, in India, corporations like Toyota, Ford and Hyundai have led to availability of cars from other countries which are of high quality.
(ii) MNCs from developing countries are also increasing their presence in developed countries. For example, Tata Tea purchased Tetley, a tea brand in Britain a few years ago.
(iii) They have led to a greater movement of labor across the world. For example, Indian software engineers working in TCS go to the U.S. for work.
(iv) MNCs have increased the inflow of foreign capital across different countries. For example, when a corporation like General Electric invests in India, it brings in capital from abroad.
(v) They have led to more transfer of technology across the countries. For example, Samsung brings in more advanced technology for manufacturing electronics into countries like India.
OR
Technology has been the most important factor in triggering globalisation. It has been the main catalyst for its advancement.
For Example, the internet and information systems. Massive amounts of information and data are available via the World Wide Web. The obvious benefits have been as follows-
(a) The world’s banking systems have benefited from the ability to instantly transfer funds, simplifying long-distance transactions.
(b) Most global businesses use technology that has been available for many years, such as planes and ships. However, innovative navigation advancements, such as global positioning systems, have increased efficiency and made travel safer.
(c) In cargo handling our ports have become safer and more efficient. With the improvement in infrastructure and better engineered vehicles domestic cargo movement (and passenger movement) has become safer and efficient.
SECTION – D
11. Read the given text and answer the following questions :
As cotton industries developed in England, industrial groups began worrying about imports from other countries. They pressurised the government to impose import duties on cotton textiles so that Manchester goods could sell in Britain without facing any competition from outside. At the same time industrialists persuaded the East India Company to sell British manufactures in Indian markets as well. Exports of British cotton goods increased dramatically in the early nineteenth century. At the end of the eighteenth century there had been virtually no import of cotton piece-goods into India. But by 1850 cotton piece-goods constituted over 31 per cent of the value of India imports; and by the 1870s this figure was over 50 per cent.
Cotton weavers in India thus faced two problems at the same time: their export market collapsed, and the local market shrank, being glutted with Manchester imports. Produced by machines at lower costs, the imported cotton goods were so cheap that weavers could not easily compete with them. By the 1850s, reports from most weaving regions of India narrated stories of decline and desolation.
11.1 In which century exports of British cotton goods increased dramatically ?
Answer : Nineteenth Century
11.2 Why Manchester imports were cheap?
Answer : They were produced by machine.
11.3 Which led to the decline of Indian cotton textiles in the early 19th Century?
Answer : As cotton industries developed in England, they pressurised the government to impose import duties on cotton textiles, so that Manchester goods could sell in Britain without giving any competition from outside.
12. Read the given text and answer the following questions :
Manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of development in general and economic development in particular mainly because–
Manufacturing industries not only help in modernizing agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas. Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible. Agriculture and industry are not exclusive of each other. They move hand in hand. For instance, the agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity. They depend on the latter for raw materials and sell their products such as irrigation pumps, fertilizers, insecticides, pesticides, plastic and PVC pipes, machines and tools, etc. to the farmers.
12.1 How does the manufacturing industry help other sectors of the economy?
Answer : Manufacturing sector is considered as the backbone of development. Manufacturing actively helps in the development of other sectors of the economy in the following ways–
(a) Manufacturing sector provides various implements and inputs to agriculture such as pumps, tractor, fertilisers, pesticides, etc. Further agro- industry has given big boost to agriculture.
(b) Once there is manufacturing the products have to be distributed quickly to various parts of the country. Thus, manufacturing stimulates the services sector as well.
12.2 How does industrial development help in reducing poverty?
Answer : Industrial development leads to job creation which leads to better earning for a large number of people. That is why we see that industrial belts have better prosperity. In general, when raw materials are converted to industrial goods more economic value is generated. The world over industrialisation has led to eradication of unemployment and poverty.
12.3 Industrialisation helps to earn foreign exchange; How?
Answer : Export of manufacturing goods expands trade and commerce and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
SECTION – E
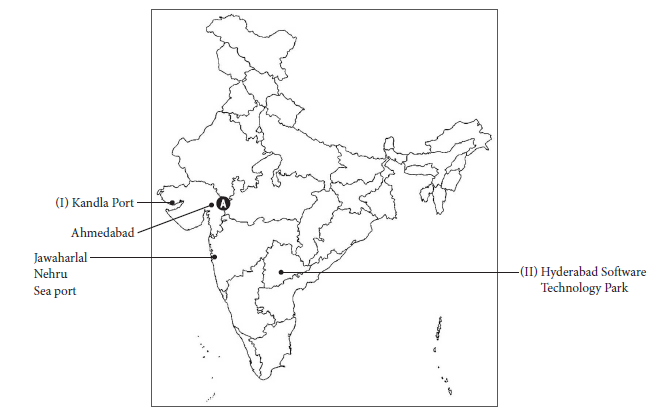
13. 13.1 On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it.
(A) The place where Mahatma Gandhi started movement for cotton mill textile workers.
13.2 On the same outline map of India locate and label of the following with suitable symbols.
(I) Kandla Port
OR
Jawaharlal Nehru Seaport
(II) Hyderabad Software Technology Park
Answer :