Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies
Please see below Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies with solutions. These CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies will help you to gain more understanding of the examination style and expected paper pattern. Students should practice the below Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies with answers provided below. We have provided all sample papers for Standard 12 for free.
| Class 12 Business Studies Sample Paper Term 1 |
| Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 1 Set A |
| Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 1 Set B |
| Class 12 Business Studies Sample Paper Term 2 |
| Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 2 Set A |
| Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 2 Set B |
| Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 2 Set C |
| Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 2 Set D |
Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 2 Set A
1. Kiran has started a business after completing a course in textile designing. She has tied up with an e-commerce company for supplying to them good quality designer clothes like kurtas, sarees, etc.
She believes that controlling without planning is blind. So, every time she gets an order, she sets the standards in terms of the number of personnel required, the estimated requirements in man-hours per product, the requirements of direct materials for the projected production and the amount of normal overhead expenses required at the projected work-load. She also keeps a close watch on the activities so as to ensure that they are according to plans. Whenever the order size is too large, she hires extra workers by placing a notice on the notice-board of the factory specifying the details of the jobs available.
Which method of recruitment is being used by Kiran to hire the extra workers?
Answer: Kiran has hired the extra workers through external recruitment method, i.e., direct recruitment.
Under the direct recruitment, a notice is placed on the notice-board of the enterprise specifying the details of the jobs available. Jobseekers assemble outside the premises of the organisation on the specified date and selection is done on the spot. The practice of direct recruitment is followed usually for casual vacancies of unskilled or semi-skilled jobs. Such workers are known as casual or ‘badli’ workers and they are paid remuneration on daily wage basis.
2. These days, the development of a country is also judged by its system of transferring finance from the sector where it is in surplus to the sector where it is needed the most. To give strength to the economy, SEBI is undertaking measures to develop the capital market. In addition to this, there is another market in which unsecured and short-term debt instruments are actively traded every day. These markets together help the savers and investors in directing the available funds into their most productive investment opportunity.
Identify the function being performed by the market in the above case.
Answer: Allocative function is the function being performed by the financial market in the above case. This function act as a link between the savers and investors by mobilising funds and investing them into the most productive channels.
3. Manasvi, Manager in a company using highly sophisticated machines and equipments, wants that every employee should be fully trained before using the machines and equipments. Suggest and describe the best method of training that Manasvi can use for training of the employees.
Answer: Vestibule method of training should be imparted in the given situation.
Vestibule training: Under this method, employees learn their jobs on the equipment they will be using, but the training is conducted away from the actual work floor. Actual work environment is created in a classroom and employees use the same materials, files and equipments. This is usually done when
employees are required to handle sophisticated machinery and equipment. Vestibule training is suitable where a large number of persons are to be trained at the same time for the same kind of work. The main emphasis is on learning rather than on production.
4. Kamal is an experienced manager concerned about the 3% rise in the raw materials. However, he knows that this is an acceptable range. He tells his staff that if this rise goes beyond 3% it should be brought into the notice of management. Then, he sets a limit of 5% when the management should give it the priority over other activities. Identify the step of controlling process applicable in the following case.
Answer: Analysing deviations is the step of process which is being applicable here. In this, the deviations from the standards are assessed and analysed to identify the causes of deviations.
Management by exception is the technique which is used in this case. This technique of management belief that only the essential and significant deviations that are beyond the acceptable limit should be controlled.
5. Joydeep has completed his Ph.D. from London school of economics. He observed there that the senior management more often communicated failures than successes. They rarely shared any good news related to the growth of the firm or give any recognition to its employees for their extraordinary contributions towards the firm. As a result, Joydeep never felt encouraged enough to work up to his full potential and started exploring other avenues for employment.
In the context of the above case:
(a) Identify and explain the element of directing in the absence of which the employees don’t feel encouraged to work.
(b) State the importance of this element as identified in part (a) by giving any two suitable points.
Answer: (a) The element of directing being referred to is motivation.
Motivation: It is a psychological factor that motivate employees to work effectively and efficiently to achieve organisational goals. It is a force or influence that causes someone to act or work eagerly. Employees can be motivated by triggering their psychological needs and desires of power,achievement, recognition, appreciation and love.
(b) The importance of motivation is described below:
(i) Improves performance: Motivation helps to improve the performance of both the employees as well as the organisation. This is because motivated employees contribute their maximum efforts for organisational goals.
(ii) Reduces employee turnover: Motivation helps to reduce employee turnover and thereby saves the cost of new recruitment and training. This is due to the fact that the managers identify the motivational needs of employees and provide suitable incentives. Consequently, the employees feel satisfied and may not think of leaving the organisation.
6. Explain any three features of Directing.
OR
Discuss Autocratic Style of Leadership.
Answer: The characteristics or features of direction can be explained as follows:
(a) Related to human relations: Directing involves communicating with superiors, instructing subordinates and guiding human resources across all levels of management in an organisation.
Directing aims at productively utilising all resources through appropriate means of communication.
(b) Grouped function: Directing is not a single function but a group of various functions like supervision, motivation, leadership and communication.
(c) Harmonising of objectives: This implies that directing establishes consensual coexistence of organisational and personal (individual) goals. This further implies that directing aims at avoiding conflicts across all levels of management leading to organisational success and employee satisfaction.
OR
Autocratic Leadership Style: An autocratic leader gives orders and expects his subordinates to obey those orders. If a manager is following this style, then communication is only one-way with the subordinate only acting according to the command given by the manager. This leader does not change or wish to be
contradicted. His following is based on the assumption that reward or punishment both can be given depending upon the result.
This leadership style is effective in getting productivity in many situations like in a factory where the supervisor is responsible for production on time and has to ensure labour productivity.
7. List any three factors which affect financing decision of the company.
Answer: Financing Decision is about the quantum of finance to be raised from various long-term sources. Shortterm sources are studied under the ‘working capital management’.
The factors that affect the Financing Decision are:
(a) Cost: The cost of raising funds through different sources is different. A prudent financial manager would normally opt for a source which is the cheapest.
(b) Risk: The risk associated with each of the sources is different.
(c) Floatation Costs: Higher the floatation on cost, less attractive the source.
(d) Cash Flow Position of the Company: A stronger cash flow position may make debt financing more viable than funding through equity.
8. Anil Ltd. is engaged in manufacturing auto-parts. The target production is 200 units per day. The company had been successfully attaining this target until two months ago. Over the last two months, it has been observed that daily production varies between 150-170 units.
(a) Identify the management function to rectify the above situation.
(b) Briefly state the procedure to be followed so that the actual production may come up to the target production.
Answer: (a) The controlling function of management is needed to rectify the above situation.
(b) The procedure to be followed so that the actual production may come up with the target production is as follows:
(i) Providing training to workers if the workers are not well-versed with the production process.
(ii) Improving the work environment if it is not conducive to efficient working.
(iii) Ensuring timely availability of the raw materials and other equipments if they are not made available on time.
(iv) Replacing the machinery if it is defective or has become obsolete.
9. Enumerate the reliefs available for Consumer under Consumer Protection Act, 2019?
OR
Enumerate the three tier machinery under Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
Answer: 9. Reliefs available to Consumer under Consumer Protection Act, 2019 are as follows:
(a) Removal of flaws in the goods.
(b) Removal of the deficiencies in the services.
(c) Replacement of damaged goods with new ones that is free of flaws.
(d) Refunding the complainant for the price paid by him.
(e) Payment of an appropriate amount of compensation for any loss or injury that has occurred.
(f) In suitable circumstances, payment of punitive damages.
(g) Discontinuance or abandonment unfair/restrictive trade practices.
(h) Discontinuance of the sale of hazardous goods and services.
(i) Payment to the consumer welfare fund (not less than 5%) which is to be used in the prescribed manner.
(j) Run corrective advertisements to counteract the effect of misleading advertisements.
(k) Reimburse all parties for their expenses.
OR
The three tier machinery under Consumer Protection Act 2019 are as follows:
(a) District Commission:
The state concerned establishes district forums in each district. The following are the key characteristics:
(i) It is made up of a President and two members, one of whom must be a woman, who are officially nominated by the state government.
(ii) The value of consumer complaints should not exceed ` 1 crore.
(iii) If any of the party is not satisfied with the district forum’s decision, they have 45 days to file an appeal with the state forum from the date of order.
(b) State Commission:
The government establishes a state commission in each state. The following are the key characteristics:
(i) Each commission has a president and at least two members appointed by the state government, one of whom should be a woman.
(ii) The total worth of the products or services, including the compensation sought, is greater than ` 1 Crore but less than ` 10 crore.
(iii) If any of the parties is not pleased with the judgement, they can file a complaint with the national commission within 30 days of the order being issued.
(c) National Commission:
Central government sets the National commission. The provisions are:
(i) It is made up of a President and at least four members chosen by the central government, one of whom should be a woman.
(ii) All complaints relating to products and services with a compensation value above ` 10 crores can be filed with the national commission.
(iii) The National Commission has the authority to issue orders for product replacement and loss compensation, among other things.
(iv) If any of the parties is not pleased with the decision taken, they can file a complaint with the Supreme Court of India within 30 days of the order being issued.
10. Naresh was involved in a business. He manipulated the profits of the company and conducted some fraudulent activities against SEBI guidelines. On regular inspection and by conducting enquiries of the brokers involved, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was able to detect this irregularity.
Identify the function performed by the SEBI in the above case and explain the protective function.
Answer: The function performed by the SEBI in the above case is Regulatory function.
The protective function includes the following activities:
(a) Prohibits insider trading: Insider trading is the act of buying or selling of the securities by the insiders of a company, which includes the directors, employees and promoters. To prevent such trading SEBI has barred the companies to purchase their own shares from the secondary market.
(b) Check price rigging: Price rigging is the act of causing unnatural fluctuations in the price of securities by either increasing or decreasing the market price of the stocks that leads to unexpected losses for the investors. SEBI maintains strict watch in order to prevent such malpractices.
(c) Promoting fair practices: SEBI promotes fair trade practice and works towards prohibiting fraudulent activities related to trading of securities.
11. Mr.Kanan is an H.R. Manager of “Ahuja Furniture Private Limited.” At the beginning of the new year he anticipated that the company will need 60 new additional persons to fill up different vacancies. He gave an advertisement in the newspaper inviting applications for filling up different vacant posts. As many as 120 applications were received. The same were scrutinised. Out of these, conditions of 15 applicants were not acceptable to the company. Letters of regret, giving reasons, were sent to them. Remaining candidates were called for preliminary interview. The candidates called for were asked to fill up blank application forms. Thereafter, they were given four tests. The objective of the first test was to find out how much interest the applicant takes in his work. The objective of the second test was to find out ‘specialisation’ of the applicant in any particular area. Third test aimed at making sure whether the applicant was capable of learning through training or not. The purpose of the fourth test was to find out how much capability a person has to mix-up with other persons, and whether he can influence other persons and get influenced by them.
(a) Identify the function of management performed by Mr. Karan.
(b) Identify and explain different types of tests organised in the organisation from the paragraph.
Answer: (a) The function of management performed by Mr. Kanan here is Staffing. Staffing is placing right people at right place.
(b) Intelligence Test: “First test was to find out how much interest the applicant takes in his work”.
Trade Test: “The objective of the second test was to find out ‘specialisation’ of the applicant in any particular area”.
Aptitude Test: “Third test aimed at making sure whether the applicant was capable of learning through training or not”.
Personality Test: “The purpose of the fourth test was to find out how much capability a person has to mix-up with other persons, and whether he can influence other persons and get influenced by them.”
12. Mr. X is running a successful business of R. K. Cement Ltd. Mr. X decided to expand his business by acquiring a Steel Factory. This required an investment of ` 80 crores. To seek advice in this matter, he called his financial advisor Mr. A who advised him about the judicious mix of equity (40%) and Debt (60%). Employ more of cheaper debt may enhance the EPS. Mr. A also suggested him to take loan from a financial institution as the cost of raising funds from financial institutions is low. Though this will increase the financial risk but will also raise the return to equity shareholders. He also apprised him that issue of debt will not dilute the control of equity shareholders. At the same time, the interest on loan is a tax deductible expense for computation of tax liability. After due deliberations with Mr.A, Mr. X decided to raise funds from a financial institution.
Discuss the concept of Financial Management as advised by Mr. X in the above situation and also discuss the factors which affect the concept advised by Mr.X.
OR
Company X ltd.
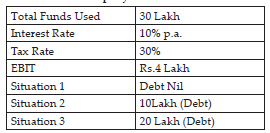
Which alternative should be used by the company in order to maximise the returns to the equity shareholders?
Answer: The concept of financial management advised by Mr.X is Capital Structure.
Capital Structure: Capital structure is defined as the combination of equity and debt that is put into use by a company in order to finance the overall operations of the company and for its growth. It can be calculated as debt-equity ratio, i.e., Debt/Equity or as the proportion of debt out of the total capital
i.e., Debt /(Debt+ Equity). Debt and equity differ significantly in their cost and riskiness for the firm. The cost of debt is lower than the cost of equity for a firm because the lender’s risk is lower than the equity shareholder’s risk, since the lender earns an assured return and repayment of capital and, therefore, they should require a lower rate of return.
Factors affecting the Choice of Capital Structure are:
(a) Cash Flow Position: Size of projected cash flows must be considered before borrowing. Cash flows must not only cover fixed cash payment obligations but there must be sufficient buffer also. It must be kept in mind that a company has cash payment obligations for (i) normal business operations;
(ii) for investment in fixed assets; and (iii) for meeting the debt service commitments, i.e., payment of interest and repayment of principal.
(b) Interest Coverage Ratio (ICR): The interest coverage ratio refers to the number of times earnings before interest and taxes of a company covers the interest obligation. This may be calculated as follows: ICR = EBIT Interest.
The higher the ratio, lower shall be the risk of company failing to meet its interest payment obligations.
(c) Debt Service Coverage Ratio: Debt Service Coverage Ratio takes care of the deficiencies referred to in the Interest Coverage Ratio (ICR). The cash profits generated by the operations are compared with the total cash required for the service of the debt and the preference share capital. A higher DSCR indicates better ability to meet cash commitments and consequently, the company’s potential to increase debt component in its capital structure.
(d) Return on Investment (RoI): If the RoI of the company is higher, it can choose to use trading on equity to increase its EPS, i.e., its ability to use debt is greater.
(e) Cost of debt: A firm’s ability to borrow at a lower rate increases its capacity to employ higher debt.
OR
Company X Ltd.

According to this table, Company X Ltd. Should go for third situation as in that case EPS is highest.

