Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 2 Set C
Please refer to Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 2 Set C with solutions provided below. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies as per the latest paper pattern and examination guidelines for Standard 12 Business Studies issued by CBSE for the current academic year. The below provided Sample Guess paper will help you to practice and understand what type of questions can be expected in the Class 12 Business Studies exam.
CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies for Term 2 Set C
Short Answer Type Questions – I
1. Identify the aspects of staffing which are concerned with upgradation of knowledge and skills of the employees?
Answer. Training helps employees to improve their knowledge and skill to make them perform their tasks more efficiently. It also helps them in promotion and improves their attitudes and confidence levels. Development refers to an information process which mainly improves the overall growth of the employees. Training and Development is an attempt to improve the current or future employee performance by increasing an employee’s ability to perform through learning, usually by changing the employee’s attitude or increasing his or her skills and knowledge.
2. Rishu’s friend Devina works as a Finance Manager in Perfect Solutions Ltd. Devina in a meeting with the directors of the company came to know that the firm would soon be declaring a bonus issue which would lead to an increase in the price of shares. On this basis, Devina advised Rishu to purchase the shares of Perfect Solutions Ltd., who thus bought the shares. Identify the function of SEBI which can control malpractices like these.
Answer. The protective function implies the role that SEBI plays in protecting the investor interest and also that of other financial participants. Prohibition of fraudulent and unfair trade practices like making misleading statements, manipulations, price rigging, insider trading etc. is the function of SEBI.
3. Explain the first two steps in the process of selection.
Answer. The first two steps in the process of selection are as follows:
(i) Preliminary Screening: Preliminary screening helps the manager eliminate unqualified or unfit job seekers based on the information supplied in the application forms. Preliminary interviews help reject misfits for reasons, which did not appear in the application forms.
(ii) Selection Tests: An employment test is a mechanism (either a paper and pencil test or an exercise) that attempts to measure certain characteristics of individuals. These characteristics range from aptitudes, such as manual dexterity, to intelligence to personality
4. A.S. Ltd. is a large company engaged in the assembly of air-conditioners. Recently the company had conducted the ‘Time’ and ‘Motion’ study and concluded that on an average, a worker can assemble ten air conditioners in a day. The target volume of the company in a day is assembling 1,000 units of air-conditioners. The company is providing attractive allowances to reduce labour turnover and absenteeism. All the workers are happy. Even then the assembly of air-conditioners per day is 800 units only. To find out the reason the company compared actual performance of each worker and observed through C.C.T.V. that some of the workers were busy in wasting time by gossiping. Identify and explain the function of Management discussed above.
Answer. Controlling: Controlling is one of the important functions performed by a manager. In order to seek planned results from the subordinates, a manager needs to exercise effective control over the activities of the subordinates. In other words, controlling means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as per the plans. Controlling also ensures that an organization’s resources are being used effectively and efficiently for the achievement of predetermined goals. Controlling is, thus, a goaloriented function.
Short Answer Type Questions – II
5. Hema is a permanent employee of a very large company called Global Pvt. Ltd. She has been working with the company for the last 5 years and is now eligible for retirement benefits as well. She likes her work and performs her responsibilities with due diligence. She has always displayed utmost dedication while being at work. As per the job agreement, she had to work for 40 hours per week and was free to work overtime. Hema worked overtime during the weekdays and on some occasions, she also used to work on weekends for 8 to 10 hours. On account of which she fell sick and had to take leave from her work as she got hospitalized for a fairly long period of time. The company did not show any concern and neither did it enquire about her health. She realized that on the one hand, she was able to fulfill only some of her needs as she only had the stability of income and pension plans since she had already completed 5 years already with the organization. On the other hand, some other needs still remained unfulfilled which she realized on account of the indifferent attitude of the company during her sickness. Thus, Hema felt that though her most basic needs are being met as per Maslow’s need hierarchy theory, she has a long way to go before her highest level needs are met.
Explain the needs of Hema which are being fulfilled and not being fulfilled in the above case.
Answer. The need of Hema which is being fulfilled is security needs. Once an individual’s physiological needs are satisfied, the needs for security and safety become salient. People want to experience order, predictability and control in their lives. These needs can be fulfilled by the family and society (e.g. police, schools, business and medical care).
The need of Hema which is not being fulfilled is belongingness Needs and Esteem Needs. Belonging needs refer to affection, sense of belongingness, acceptance and friendship. Esteem needs include factors such as self-respect, autonomy status, recognition and attention.
6. Explain briefly how Directing:
(i) Facilitates introduction of needed changes in the organization.
(ii) Brings stability and balance in the organization
OR
Briefly explain the any two elements of Directing.
Answer. (i) Directing facilitates introduction of needed changes in the organization. Generally, people have a tendency to resist changes in the organization. Effective directing through motivation, communication and leadership helps to reduce such resistance and develop required cooperation in introducing changes in the organization. For example, if a manager wants to introduce new system of accounting, there may be initial resistance from accounting staff. But, if the manager explains the purpose, provides training and motivates with additional rewards, the employees may accept change and cooperate with manager.
(ii) Effective directing helps to bring stability and balance in the organisation since it fosters cooperation and commitment among the people and helps to achieve balance among various groups, activities and the departments.
OR
The elements of Directing are as follows:
(i) Motivation: Motivation means incitement or inducement to act or perform. In the context of an organization, it means the process of making subordinates to act in a desired manner to achieve certain organizational goals. It is the process of stimulating people to action in order to accomplish desired goals of the firm. It is an internal feeling of an employee and leads to goaldirected attitudes and behavior. Motivation depends primarily on the needs of individuals. It helps individuals and groups in the enterprise to give improved performance.
(ii) Leadership: It is the process of persuading people to strive willingly for group goals and objectives. A good leader should have many qualities. Some of them are courage, will power, conviction judgement, enthusiasm, knowledge, integrity, confidence, etc. Though in reality, all these qualities cannot be present in a single person and at times do not always contribute to success.
(iii) Communication: Communication refers to process of exchange of information and ideas between or among people that creates an understanding. The process of communication involves the elements of source, message encoding, channel, receiver, decoding and feedback.In all organizations, formal and informal communication takes place simultaneously.
7. Explain briefly any three factors that affect the working capital requirements of a company.
Answer. Factors affecting the working capital requirements of a company are as follows:
(i) Nature of Business: The basic nature of a business influences the amount of working capital required. A trading organization usually needs a smaller amount of working capital compared to a manufacturing organization. This is because there is usually no processing. Therefore, there is no distinction between raw materials and finished goods. Sales can be effected immediately upon the receipt of materials, sometimes even before that. In a manufacturing business, however, raw material needs to be converted into finished goods before any sales become possible. Other factors remaining the same, a trading business requires less working capital. Similarly, service industries which usually do not have to maintain inventory require less working capital.
(ii) Scale of Operations: For organizations which operate on a higher scale of operation, the quantum of inventory and debtors required is generally high. Such organizations, therefore, require large amount of working capital as compared to the organizations which operate on a lower scale.
(iii) Business Cycle: Different phases of business cycles affect the requirement of working capital by a firm. In case of a boom, the sales as well as production are likely to be larger and, therefore, larger amount of working capital is required. As against this, the requirement for working capital will be lower during the period of depression as the sales as well as production will be less.
(iv) Seasonal Factors: Most business has some seasonality in their operations. In peak season, because of higher level of activity, larger amount of working capital is required. As against this, the level of activity as well as the requirement for working capital will be lower during the lean season.
(v) Production Cycle: Production cycle is the time span between the receipt of raw material andtheir conversion into finished goods. Some businesses have a longer production cycle while some have a shorter one. Duration and the length of production cycle, affects the amount of funds required for raw materials and expenses. Consequently, working capital requirement is higher in firms with longer processing cycle and lower in firms with shorter processing cycle.
(vi) Credit Allowed: Different firms allow different credit terms to their customers. This depends upon the level of competition that a firm faces as well as the credit worthiness of their clientele A liberal credit policy results in higher amount of debtors, increasing the requirement of working capital.
(vii) Credit Availed: Just as a firm allows credit to its customers it also may get credit from its suppliers. To the extent it avails credit on purchases; the working capital requirement is reduced.
(viii) Operating Efficiency: Firms manage their operations with varied degrees of efficiency. For example, a firm managing its raw materials efficiently may be able to manage with a smaller balance. This is reflected in a higher inventory turnover ratio. Similarly, a better debtor’s turnover ratio may be achieved by reducing the amount tied up in receivables. Better sales effort may reduce the average time for which finished goods inventory is held. Such efficiencies may reduce the level of raw materials, finished goods and debtors resulting in lower requirement of working capital.
(ix) Availability of Raw Material: If the raw materials and other required materials are available freely and continuously, lower stock levels may suffice. If, however, raw materials do not have a record of un-interrupted availability, higher stock levels may be required. In addition, the time lag between the placement of order and the actual receipt of the materials (also called lead time) is also relevant. Larger the lead time, larger the quantity of material to be stored and larger shall be the amount of working capital required.
(x) Growth Prospects: If the growth potential of a concern is perceived to be higher, it will require larger amount of working capital so that it is able to meet higher production and sales target whenever required.
(xi) Level of Competition: Higher level of competitiveness may necessitate larger stocks of finished goods to meet urgent orders from customers. This increases the working capital requirement. Competition may also force the firm to extend liberal credit terms discussed earlier.
(xii) Inflation: With rising prices, larger amounts are required to maintain a constant volume of production and sales. The working capital requirement of a business thus, becomes higher with higher rate of inflation.
8. A critical point control (CPC) approach is followed by Mc Donald’s in the cooking and handling process so that any food safety threat can be prevented, eliminated, or reduced to an acceptable level. Hence, continuous monitoring of activities is undertaken to ensure that the process is right at each critical point control. The main principle followed for cooking at Mc Donald’s is “fewer amounts much time” which can ensure the high quality and increased freshness level of the food. For instance, if four hamburgers have to be made, a worker cannot cook all the four hamburgers at one time. The time figured out for making one hamburger is one hundred and forty-five seconds. Moreover, nearly all foods in items the Mc Donald’s have a specific holding time, the holding time for hamburgers is ten minutes and for French fries it is seven minutes. If it is not sold within that time it is thrown away. Also, the temperature of the milk sent by the supplier must be under 4° C, otherwise, it will be returned.
(i) Identify and explain the steps in the process of controlling discussed in the above case.
(ii) Identify and explain any one point which highlights the importance of the controlling function in the above text.
Answer. (i) Following are the steps discussed in the case:
(a) Analyzing Deviations: Some deviation in performance can be expected in all activities. It is, therefore, important to determine the acceptable range of deviations. Also, deviations in key areas of business need to be attended more urgently as compared to deviations in certain insignificant areas. Critical point control and management by exception should be used by a manager in this regard.
(b) Taking Corrective Action: No corrective action is required when the deviations are within acceptable limits. However, when the deviations go beyond the acceptable range, especially in the important areas, it demands immediate managerial attention so that deviations do not occur again and standards are accomplished. Corrective action might involve training of employees if the production target could not be met. Similarly, if an important project is running behind schedule, corrective action might involve assigning
of additional workers and equipment to the project and permission for overtime work.
(ii) Following are the point which highlights the importance of the controlling function in the above text:
(a) Accomplishing organizational goals: The controlling function measures progress towards the organizational goals and brings to light the deviations, if any, and indicates corrective action to be taken. It, thus, guides the organization and keeps it on the right track so that organizational goals can be achieved.
(b) Making efficient use of resources: By exercising control, a manager seeks to reduce wastage and spoilage of resources. Each activity is performed in accordance with predetermined standards and norms. This ensures that resources are used in the most effective and efficient manner.
(c) Judging accuracy of standards: A good control system enables management to verify whether the standards set are accurate and objective. An efficient control system keeps a careful check on the changes taking place in the organization and in the environment and helps to review and revise the standards in light of such changes.
Long Answer Type Questions
9. What is meant by ‘Consumer Protection’? Explain three points of importance of consumer protection from the point of view of consumers.
OR
Define ‘consumer’ according to the provisions of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019. Who can file a complaint?
Answer. Meaning of Consumer Protection: Consumer protection means the act of providing adequate protection to consumers against the unscrupulous, exploitative and unfair trade practices of manufacturers and service providers. The importance of consumer protection from the consumers’ point of view can be understood from the following points:
(i) Consumer Ignorance: In the light of widespread ignorance of consumers about their rights and reliefs available to them, it becomes necessary to educate them about the same so as to achieve consumer awareness.
(ii) Unorganized Consumers: Consumers need to be organized in the form of consumer organizations which would take care of their interests. Though, in India, we do have consumer organizations which are working in this direction, adequate protection is required to be given to consumers till these organizations become powerful enough to protect and promote the interests of consumers.
(iii) Widespread Exploitation of Consumers: Consumers might be exploited by unscrupulous, exploitative and unfair trade practices like defective and unsafe products, adulteration, false and misleading advertising, hoarding, black-marketing etc. Consumers need protection against such malpractices of the sellers.
OR
Under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, a consumer is defined as:
(i) Any person who buys any goods for a consideration, which has been paid or promised, or partly paid and partly promised, or under any scheme of deferred payment. It includes any user of such goods, when such use is made with the approval of the buyer, but does not include a person who obtains goods for resale or any other commercial purpose.
(ii) Any person who hires or avails any service, for a consideration which has been paid or promised, or partly paid and partly promised, or under any system of deferred payment. It includes any beneficiary of services when such services are availed of with the approval of the person concerned, but does not include a person who avails such services for any commercial purpose.
A complaint can be filed by any of the following:
(a) One or more consumer on behalf of numerous consumer
(b) Any consumer
(c) Any registered Consumer’s Association
(d) Government
(e) Legal heirs of a deceased consumer
10. “To promote orderly and healthy growth of the securities market and protection of the investors, Securities and Exchange Board of India was set up.” With reference to this statement, explain the objectives of Securities and Exchange Board of India.
Answer. Objectives of SEBI are:
(i) To regulate stock exchanges and the securities industry in order to promote their orderly functioning.
(ii) To protect the rights and interests of the investors, particularly individual investors and to guide and educate them.
(iii) To prevent trading malpractices and achieve a balance between self-regulation and statutory regulation.
(iv) To regulate and develop a code of conduct and fair practices by intermediaries like brokers, merchant bankers, etc. with a view to making them competitive and professional.
(v) To provide a market place in which the issuers can raise finances in an easy, fair and efficient manner.
(vi) To create an environment to facilitate efficient mobilisation and allocation of resources.
11. There were two vacancies for the post of Assistant Manager in ‘Gyan Electrics Private Ltd.’ Parth, the Human Resources Manager identified one suitable candidate Vishwas from within the organization and promoted him to the post of Assistant Manager. For another post, the Manager Parth took help of a placement agency and selected Saleem. After six months, Parth observed that Vishwas’s performance was much better than Saleem’s performance though Vishwas was less qualified than Saleem. Hence, Parth decided that in future he will not make any appointment with the help of an outside source. Explain any five reasons on the basis of which Parth would have taken the above decision.
Answer. Reasons on the basis of which ‘Parth’ would have taken the decision not to make appointment with the help of an outside source are:
(i) Employees are motivated to improve their performance. A promotion at a higher level may lead to a chain of promotion at lower levels in the organization. This motivates the employees to improve their performance through learning and practice. Employees work with commitment and loyalty and remain satisfied with their jobs. Also peace prevails in the enterprise because of promotional avenues
(ii) Internal recruitment also simplifies the process of selection and placement. The candidates that are already working in the enterprise can be evaluated more accurately and economically. This is a more reliable way of recruitment since the candidates are already known to the organization
(iii) Transfer is a tool of training the employees to prepare them for higher jobs. Also people recruited from within the organization do not need induction training
(iv) Transfer has the benefit of shifting workforce from the surplus departments to those where there is shortage of staff
(v) Filling of jobs internally is cheaper as compared to getting candidates from external sources.
12. Samrat International Ltd. earned a net profit of ₹ 250 crore. Suhani, the finance manager of Samrat International Ltd., wants to decide how to appropriate these profits. Identify the decision that Suhani will have to take and also discuss any four factors which help her in taking this decision.
OR
‘Smart Stationery Ltd.’ wants to raise funds of ₹ 40,00,000 for its new project. The management is considering the following mix of debt and equity to raise this amount:
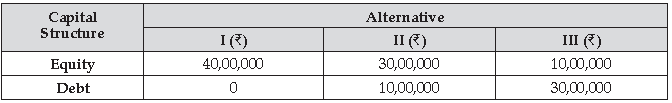
Other details are as follows:
Interest Rate on Debt = 9%
Face Value of Equity Shares = 100 each
Tax Rate = 30%
Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) = 8,00,000
(i) Under which of the three alternatives will the company be able to take advantage of Trading on Equity?
(ii) Does Earning Per Share always rise with increase in debt? Give reasons to support your answer.
Answer. (i) Dividend Decision
(ii) Factors affecting dividend decision are as follows:
(a) Earnings: The dividend is paid out of the current and reserved profits. Therefore, any firm with greater amount of total profit will ensure greater dividend to its shareholders.
(b) Stability of earnings: Other things remaining the same, a company having stable earning is in a better position to declare higher dividends. As against this, a company having unstable earnings is likely to pay smaller dividend.
(c) Stability of dividend: Companies generally follow a policy of stabilizing dividend per share. The increase in dividends is generally made when there is confidence that their earning potential has gone up and not just the earnings of the current year. In other words, dividend per share is not altered if the change in earnings is small or seen to be temporary in nature.
(d) Growth opportunities: Companies having good growth opportunities retain more money out of their earnings so as to finance the required investment. The dividend in growth companies is, therefore, smaller, than that in the non– growth companies.
(e) Cash flow position: The payment of dividend involves an outflow of cash. A company may be earning profit but may be short on cash. Availability of enough cash in the company is necessary for declaration of dividend.
(f) Stock market reactions: Investors, in general, view an increase in dividend as good news and stock prices react positively to it. Similarly, a decrease in dividend may have a negative impact on the share prices in the stock market. Thus, the possible impact of dividend policy on the equity share price is one of the important factors considered by the management while taking a decision about it.
(g) Shareholders’ preference: While declaring dividends, managements must keep in mind the preferences of the shareholders in this regard. If the shareholders in general desire that at least a certain amount is paid as dividend, the companies are likely to declare the same. There are always some shareholders who depend upon a regular income from their investments.
(h) Taxation policy: The choice between the payment of dividend and retaining the earnings is, to some extent, affected by the difference in the tax treatment of dividends and capital gains. If tax on dividend is higher, it is better to pay less by way of dividends. As compared to this, higher dividends may be declared if tax rates are relatively lower. Though the dividends are free of tax in the hands of shareholders, a dividend distribution tax is levied on companies.
(i) Access to capital market: Large and reputed companies generally have easy access to the capital market and, therefore, may depend less on retained earnings to finance their growth. These companies tend to pay higher dividends than the smaller companies which have relatively low access to the market.
(j) Legal constraints: Certain provisions of the Companies Act place restrictions on dividend declaration and payout of dividend. These provisions have to be given due consideration while declaring dividend.
(k) Contractual constraints: Many times while granting loans to a company, the lender may impose certain restrictions on the payment of dividends in future in order to ensure that the company has sufficient funds to repay his loan, which should not be violated by the company.
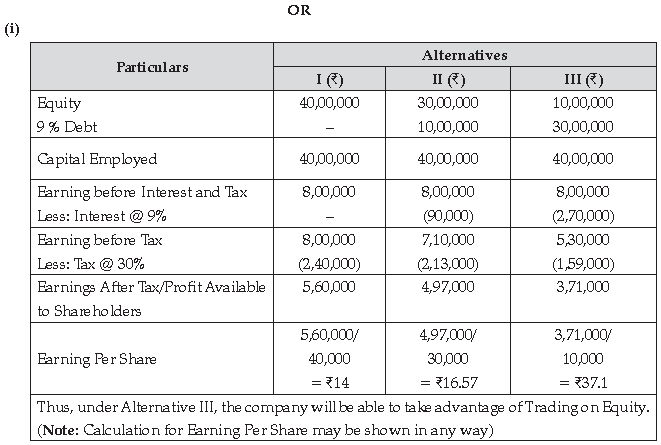
(ii) No, Earning Per Share does not always rise with increase in debt. EPS decreases when the company cannot earn greater profit than the value of debt.
