Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 2 Set D
Please refer to Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies Term 2 Set D with solutions provided below. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies as per the latest paper pattern and examination guidelines for Standard 12 Business Studies issued by CBSE for the current academic year. The below provided Sample Guess paper will help you to practice and understand what type of questions can be expected in the Class 12 Business Studies exam.
CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Business Studies for Term 2 Set D
Short Answer Type Questions – I
1. Identify and explain the function of management which begins with workforce planning and includes different other functions like recruitment, selection, training, development, promotion, compensation and performance appraisal of work force.
Answer. Staffing is the function of management which begins with workforce planning and includes different other function like recruitment, selection, training, development, promotion, compensation and performance appraisal of work force. In other words, staffing is that part of the process of management which is concerned with obtaining, utilizing and maintaining a satisfactory and satisfied work force. Staffing has been described as the managerial function of filling and keeping filled the positions in the organization structure. This is achieved by, first of all, identifying requirement of work force, followed by recruitment, selection, placement, promotion, appraisal and development of personnel, to fill the roles designed into the organization structure.
2. Rajni Auto Manufacturers has been into business for the last 30 years and have decided to give a special privilege to their existing shareholders to subscribe to the new issue of shares where they will be given shares according to the proportion of shares held by them. The company always gives special treatment to its loyal stakeholders and also ensures that they remain associated with the organization for longer durations. Last year, the company was successfully dealing through the capital market where both the buying and selling of securities were taking place. The owner of the company is a man of ethical business. He often contributes to business magazines by writing articles and editorials. He recently wrote an article about the watchdog of stock market. The article gained a lot of popularity and now is part of the curriculum of MBA students. Identify and explain type of capital market the company was dealing with.
Answer. The company was dealing with secondary market. The secondary market is also known as the stock market or stock exchange. It is a market for the purchase and sale of existing securities. It helps existing investors to disinvest and fresh investors to enter the market. It also provides liquidity and marketability to existing securities. It also contributes to economic growth by channelizing funds towards the most productive investments through the process of disinvestment and reinvestment. Securities are traded, cleared and settled within the regulatory framework prescribed by SEBI.
3. “An enterprise has to tap external sources for various positions because all the vacancies cannot be filled through internal recruitment.” In the light of this statement, explain any two merits of external sources of recruitment.
Answer. The advantages of using external sources of recruitment are as follows:
(i) Qualified Personnel: By using external sources of recruitment, the management can attract qualified and trained people to apply for vacant jobs in the organization.
(ii) Wider Choice: When vacancies are advertised widely, a large number of applicants from outside the organization apply. The management has a wider choice while selecting the people for employment.
(iii) Fresh Talent: The present employees may be insufficient or they may not fulfill the specifications of the jobs to be filled. External recruitment provides wider choice and brings new blood in the organization. However, it is expensive and time consuming.
(iv) Competitive Spirit: If a company brings manpower from external sources, the existing staff will have to compete with the outsiders. They will work harder to show better performance.
4. ‘Home Food’ is a company involved in the export of indigenous homemade food products like chutneys and pickles. It has tied up with the small farmers in various states for sourcing of fruits and vegetables. In this way, it helps the small farmers to sell their produce at reasonable rates. The company follows a practice where only significant deviations from a budget or plan are brought to the attention of management. The degree of deviations allowed in different categories in the budget are well defined in advance, along with the appropriate levels of management who will respond to the deviations in question. For example, a deviation of ₹30,000 or more in purchase costs will be reported to the concerned department manager. In context of the above case, Identify and explain the principle of management control adopted by the company.
Answer. Management by Exception: Management by exception, which is often referred to as control by exception, is an important principle of management. Control by exception is based on the belief that an attempt to control everything results in controlling nothing. Thus, only significant deviations which go beyond the permissible limit should be brought to the notice of management. Thus, if the plans lay down 2 per cent increase in labour cost as an acceptable range of deviation in a manufacturing organization, only increase in labour cost beyond 2 per cent should be brought to the notice of the management. However, in case of major deviation from the standard (say, 5 per cent), the matter has to receive immediate action of management on a priority basis.
Short Answer Type Questions – II
5. Zeba Ltd., an e-commerce company operating for the past 10 years, is a company which strongly believes in motivating its employees by offering them various incentives. It is so because they are very focused on their goals and objectives and want their people to improve their performance because there is a lot of competition in the market and Zeba Ltd. has the vision to become the market leader in the next 5 years. Aman, who is an alumnus of IIM Ahmedabad and has done his specialization in Marketing, is a marketing employee, employed with the company for the last 3 years has often been rewarded with a pay hike for his growing performance. Samay, who is a Chartered Accountant and has been working in the company for the last 7 years, is from the finance department and has been allotted some shares by the management in lieu of various incentives payable in cash for his continuous efforts towards ensuring timely availability of funds and their effective utilization at all times. Aadvika, who recently graduated from FMS Delhi, is working in the Human Resources department of the company and joined as a contractual employee but is now on the payrolls of the company. The company also organizes annual functions to provide public appreciation to its high performers as it strongly believes in uplifting their spirits towards working for the company as well as preventing them from joining their competitors. Identify and explain the type of incentive which has been provided to Aman, Samay and Aadvika?
Answer. The type of incentive been provided to Aman is pay and allowances. For every employee, salary is the basic monetary incentive. It includes basic pay, dearness allowance and other allowances. Salary system consists of regular increments in the pay every year and enhancement of allowances from time-to-time. In some business organizations, pay hike and increments may be linked to performance. The type of incentive been provided to Samay is Co-partnership. Under these incentive schemes, employees are offered company shares at a set price which is lower than market price. Sometimes, management may allot shares in line of various incentives payable in cash. The allotment of shares creates a feeling of ownership to the employees and makes them to contribute for the growth of the organization. The type of incentive has been provided to Aadvika is job security. Employees want their job to be secure. They want certain stability about future income and work so that they do not feel worried on these aspects and work with greater zeal. In India, this aspect is more important considering the inadequate job opportunities and too many aspirants for these. However, there is one negative aspect of job security. When people feel that they are not likely to lose their jobs, they may become complacent.
6. Define Directing. Explain by giving any two points why directing is an important function of management?
OR
What is meant by ‘Motivation’? Explain the following needs of Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory of Motivation which is considered fundamental to the understanding of motivation:
(i) Security or safety needs
(ii) Self actualization needs
Answer. Directing refers to the process of instructing, guiding, counselling, motivating and leading people in the organization to achieve its objectives: The points which emphasise the importance of directing is presented as follows:
(i) Directing initiates action: Directing helps to initiate action by people in the organization towards attainment of desired objectives. For example, if a supervisor guides his subordinates and clarifies their doubts in performing a task, it will help the worker to achieve work targets given to him.
(ii) Directing integrates employees’ efforts: Directing integrates employees’ efforts in the organization in such a way that every individual effort contributes to the organizational performance. Thus, it ensures that the individuals work for organizational goals. For example, a manager with good leadership abilities will be in a position to convince the employees working under him that individual efforts and team effort will lead to achievement of organizational goals.
(iii) Directing guides employees to realize their potential: Directing guides employees to fully realize their potential and capabilities by motivating and providing effective leadership. A good leader can always identify the potential of his employees and motivate them to extract work up to their full potential.
(iv) Directing facilitates changes: Directing facilitates introduction of needed changes in the organization. Generally, people have a tendency to resist changes in the organization. Effective directing through motivation, communication and leadership helps to reduce such resistance and develop required cooperation in introducing changes in the organization. For example, if a manager wants to introduce new system of accounting, there may be initial resistance from accounting staff. But, if manager explains the purpose, provides training and motivates with additional rewards, the employees may accept change and cooperate with manager.
(v) Directing brings stability and balance in the organization: Effective directing helps to bring stability and balance in the organization since it fosters cooperation and commitment among the people and helps to achieve balance among various groups, activities and the departments.
OR
Meaning of Motivation: Motivation means incitement or inducement to act or move. In the context of an organization, it means the process of making subordinates to act in a desired manner to achieve certain organizational goals. It is a process of stimulating and inspiring people in the organization to contribute to the best of their ability for the achievement of organizational goals and objectives.
(i) Security or safety needs: These refer to the needs for physical safety, protection and economic security which include safety of person and property and come into picture only when physiological needs are satisfied.
(ii) Self actualization needs: It refers to the highest level of need in the hierarchy. It deals with the drive to become what one is capable of becoming by attaining one’s true potential and includes growth, self-fulfillment, etc.
7. What is meant by Financial Planning? State any two points of its importance.
Answer. The process of estimating the fund requirements of a business and specifying the sources of funds is called Financial Planning. Financial planning is the preparation of a financial blueprint of an organization’s future operations. The objective of financial planning is to ensure that enough funds are available at right time. If adequate funds are not available the firm will not be able to honour its commitments and carry out its plans.
The importance of financial planning can be explained as follows:
(i) It helps in forecasting what may happen in future under different business situations. By doing so, it helps the firms to face the eventual situation in a better way. In other words, it makes the firm better prepared to face the future. For example, a growth of 20% in sales is predicted. However, it may happen that the growth rate eventually turns out to be 10% or 30%. Many items of expenses shall be different in these three situations. By preparing a blueprint of these three situations the management may decide what must be done in each of these situations. This preparation of alternative financial plans to meet different situations is clearly of immense help in running the business smoothly.
(ii) It helps in avoiding business shocks and surprises and helps the company in preparing for the future.
(iii) It helps in coordinating various business functions, e.g., sales and production functions, by providing clear policies and procedures.
(iv) Detailed plans of action prepared under financial planning reduce waste, duplication of efforts, and gaps in planning.
(v) It tries to link the present with the future.
(vi) It provides a link between investment and financing decisions on a continuous basis. (vii) By spelling out detailed objectives for various business segments, it makes the evaluation of actual performance easier.
8. Vinay was the Chief Operating Officer of ‘Easy Solutions Ltd.’, a company providing advanced software solutions to Indian Defence Services. They had been carrying on business successfully for the last twelve years and earning enough profits. But from the last one year, they realized that though the business is getting big orders which are being fulfilled on time, even then the revenues kept on decreasing. Vinay was not able to find out where the problem was. He started keeping a close check on the progress of activities as he could sense that something was wrong. He wanted to take some action before any major damage happen to the business. Vinay appointed a cyber security expert who monitored the company’s processes and found out that the computer operator was deleting the entries from the computers and pocketing the revenues. He was caught and handed over to the police. This created an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organization and helped in minimizing dishonest behavior on the part of the employees.
(i) Identify and explain the function of management discussed in the above case.
(ii) Also, in context of the above case, explain the importance of the function of management
stated in point (i).
Answer. (i) The function of management discussed in the given case is controlling.
Controlling is one of the important functions of a manager. In order to seek planned results from the subordinates, a manager needs to exercise effective control over the activities of the subordinates. In other words, controlling means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as per the plans. Controlling also ensures that an organization’s resources are being used effectively and efficiently for the achievement of predetermined goals. Controlling is, thus, a goal-oriented function.
(ii) Ensuring order and discipline: Controlling creates an atmosphere of order and discipline in the organization. It helps to minimise dishonest behavior on the part of the employees by keeping a close check on their activities.
Long Answer Type Questions
9. Explain the three-tier machinery under ‘The Consumer Protection Act’ for redressal of consumers’ grievances.
OR
Explain any five rights of consumers that has been provided by the Consumer Protection Act.
Answer. The three-tier machinery under the Consumer Protection Act for redressal of consumers grievances consists of:
(i) District Commission: The District Commission consists of a President and two other members, one of whom should be a woman. They all are appointed by the State Government concerned. A complaint can be made to the appropriate District Commission when the value of the goods or services in question, along with the compensation claimed, does not exceed Rs. 1 crore. On receiving the complaint, the District Commission shall refer the complaint to the party against whom the complaint is filed. If required, the goods or a sample thereof, shall be sent for testing in a laboratory. The District Commission shall pass an order after considering the test report from the laboratory and hearing the party against whom the complaint is filed. In case the aggrieved party is not satisfied with the order of the District Commission, he can appeal before the State Commission within 45 days of the passing of the order.
(ii) State Commission: Each State Commission consists of a President and not less than four other members, one of whom should be a woman. They are appointed by the State Government concerned. A complaint can be made to the appropriate State Commission when the value of the goods or services in question, along with the compensation claimed, exceeds Rs. 1 crore but does not exceed Rs. 10 crore. The appeals against the orders of a District Commission can also be filed before the State Commission. On receiving the complaint, the State Commission shall refer the complaint to the party against whom the complaint is filed. If required, the goods or a sample thereof, shall be sent for testing in a laboratory. The State Commission shall pass an order after considering the test report from the laboratory and hearing the party against whom the complaint is filed. In case the aggrieved party is not satisfied with the order of the State Commission, he can appeal before the National Commission within 30 days of the passing of the order.
(iii) National Commission: The National Commission consists of a President and at least four other members, one of whom should be a woman. They are appointed by the Central Government. A complaint can be made to the National Commission when the value of the goods or services in question, along with the compensation claimed, exceeds Rs. 10 crore. The appeals against the orders of a State Commission can also be filed before the National Commission. On receiving the complaint, the National Commission shall refer the complaint to the party against whom the complaint is filed. If required, the goods or a sample thereof, shall be sent for testing in a laboratory. The National Commission shall pass an order after considering the test report from the laboratory and hearing the party against whom the complaint is filed.
OR
Following are the consumer rights discussed:
(i) Right to Safety: The consumer has a right to be protected against goods and services which are hazardous to life and health. For instance, electrical appliances which are manufactured with substandard products or do not conform to the safety norms might cause serious injury. Thus, consumers are educated that they should use electrical appliances which are ISI marked as this would be an assurance of such products meeting quality specifications.
(ii) Right to be Informed: The consumer has a right to have complete information about the product he intends to buy including its ingredients, date of manufacture, price, quantity, directions for use, etc. It is because of this reason that the legal framework in India requires the manufacturer’s to provide such information on the package and label of the product.
(iii) Right to Choose: The consumer has the freedom to choose from a variety of products at competitive prices. This implies that the marketers should offer a wide variety of products in terms of quality, brand, prices, size, etc. and allow the consumer to make a choice from amongst these.
(iv) Right to be Heard: The consumer has a right to file a complaint and to be heard in case of dissatisfaction with a good or a service. It is because of this reason that many enlightened business firms have set up their own consumer service and grievance cells. Many consumer organizations are also working towards this direction and helping consumers in redressal of their grievances.
(v) Right to seek Redressal: The consumer has a right to get relief in case the product or service falls short of his expectations. The Consumer Protection Act provides a number of reliefs to the consumers including replacement of the product, removal of defect in the product, compensation paid for any loss or injury suffered by the consumer, etc.
(vi) Right to Consumer Education: The consumer has a right to acquire knowledge and to be a well-informed consumer throughout life. He should be aware about his rights and the reliefs available to him in case of a product or service falling short of his expectations. Many consumer organizations and some enlightened businesses are taking an active part in educating consumers in this respect.
10. State any three objectives and two developmental functions of Securities and Exchange Board of India.
Answer. Objectives of SEBI are:
(i) To regulate stock exchanges and the securities industry to promote their orderly functioning.
(ii) To protect the rights and interests of the investors, particularly individual investors and to guide and educate them.
(iii) To prevent trading malpractices and achieve a balance between self-regulation and statutory regulation.
(iv) To regulate and develop a code of conduct and fair practices by intermediaries like brokers, merchant bankers, etc. with a view of making them competitive and professional.
(v) To provide a market place in which the issuers can raise finances in an easy, fair and efficient manner.
(vi) To create an environment to facilitate efficient mobilisation and allocation of resources.
Development Functions of SEBI:
(i) Training of intermediaries of the securities market.
(ii) Conducting research and publishing information useful to all market participants.
(iii) Undertaking measures to develop the capital markets by adapting a flexible approach.
11. Motorcycles Rides Pvt. Ltd. decided to modernize the plant as they are going to manufacture on large scale and cater to the export market as well as the domestic market. So, it has become necessary to provide knowledge and skills to the existing workers to cope with new technology. The company believes that training will help its workers to improve their functioning and performance in many areas. Thus, the company has decided to train its workers so as to equip them with the latest production technology. But the company is in a dilemma with respect to the training method to be adopted. The HR department wants to adopt a training method which is more suitable for a manufacturing concern than a trading concern as the workers will be involved in operating many sophisticated machines, majority of which the company is planning to import from Japan. Thus, they have decided to create actual work environments in a class room and employees to use the same materials, files and equipment in order to equip themselves with the imported new technology. Some of the employees are kept under guidance of a master worker for a prescribed period of time. This will enable firm to reduce accidents as employees will be more efficient to handle machines. They also plan to recruit more people especially fresher’s to meet the rise in demand and train them accordingly. For this purpose, they have decided to select candidates who are studying but will also work in their factory or office to acquire practical knowledge and skills.
(i) Identify and explain the training method which has been chosen by Motorcycles Rides Pvt. Ltd. to train its existing workers?
(ii) Identify and explain the training method which has been chosen by Motorcycles Rides Pvt. Ltd to train its new workers?
Answer. (i) The training method which has been chosen by Motorcycles Rides Pvt. Ltd. to train its existing workers is vestibule training. Vestibule Training: Employees learn their jobs on the equipment they will be using, but the training is conducted away from the actual work floor. Actual work environments are created in a class room and employees use the same materials, files and equipment. This is usually done when employees are required to handle sophisticated machinery and equipment.
(ii) The training method which has been chosen by Motorcycles Rides Pvt. Ltd to train its new workers is internship training. Internship Training: It is a joint programme of training in which educational institutions and business firms cooperate. Selected candidates carry on regular studies for the prescribed period. They also work in some factory or office to acquire practical knowledge and skills.
12. Mr. A. Bose is running a successful business. He is the owner of R. K. Cement Ltd. He decided to expand his business by acquiring a Steel Factory. This required an investment of ` 60 crore. To seek advice in this matter, he called his financial advisor Mr. T. Ghosh who advised him about the judicious mix of equity (40%) and Debt (60%). Employing more of cheaper debt may enhance the EPS. Mr. Ghosh also suggested him to take loan from a financial institution as the cost of raising funds from financial institutions is low. Though this will increase the financial risk but will also raise the return to equity shareholders. He also apprised him that issue of debt will not dilute the control of equity shareholders. At the same time, the interest on loan is a tax-deductible expense for computation of tax liability. After due deliberations with Mr. Ghosh, Mr. Bose decided to raise funds from a financial institution.
(i) Identify the concept of financial management as advised by Mr. Ghosh in the above situation.
(ii) Also explain any four factors that affect the concept of financial management discussed above
in point (i).
OR
BonBon Ltd. is engaged in the business of manufacturing various kinds of biscuits. They produce
4 million packets of biscuits in a day. The company has a share capital of ` 20,00,000 divided into
shares of Rs. 100 each. For expansion purpose, the company requires additional funds of ` 15,00,000.
The management is considering the following alternatives for raising funds:
Answer. (i) The concept of Financial Management as advised by Mr. Ghosh in the given situation is capital structure.
(ii) Following are the factors affecting the choice of capital structure of a company:
(a) Cash Flow Position: Size of projected cash flows must be considered before borrowing. Cash flows must not only cover fixed cash payment obligations but there must be sufficient buffer also. It must be kept in mind that a company has cash payment obligations for normal business operations; for investment in fixed assets; and for meeting the debt service commitments i.e., payment of interest and repayment of principal.
(b) Interest Coverage Ratio (ICR): The interest coverage ratio refers to the number of times earnings (before interest and taxes) of a company covers the interest obligation. The higher the ratio, lower shall be the risk of company failing to meet its interest payment obligations. However, this ratio is not an adequate measure. A firm may have a high EBIT but low cash balance. Apart from interest, repayment obligations are also relevant.
(c) Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR): Debt Service Coverage Ratio takes care of the deficiencies referred to in the Interest Coverage Ratio (ICR). The cash profits generated by the operations are compared with the total cash required for the service of the debt and the preference share capital. A higher DSCR indicates better ability to meet cash commitments and consequently, the company’s potential to increase debt component in its capital structure.
(d) Return on Investment (RoI): If the ROI of the company is higher, it can choose to use trading on equity to increase its EPS, i.e., its ability to use debt is greater.
(e) Cost of debt: A firm’s ability to borrow at a lower rate increases its capacity to employ higher debt. Thus, more debt can be used if debt can be raised at a lower rate.
(f) Tax Rate: Since interest is a deductible expense, cost of debt is affected by the tax rate. A higher tax rate makes debt relatively cheaper and increases its attraction vis-a-vis equity.
(g) Cost of Equity: Stock owners expect a rate of return from the equity which is commensurate with the risk they are assuming. When a company increases debt, the financial risk faced by the equity holders, increases. Consequently, their desired rate of return may increase. It is for this reason that a company cannot use debt beyond a point. If debt is used beyond that point, cost of equity may go up sharply and share price may decrease in spite of increased EPS. Consequently, for maximization of shareholders’ wealth, debt can be used only up to a level.
(h) Floatation Costs: Process of raising resources also involves some cost. Public issue of shares and debentures requires considerable expenditure. Getting a loan from a financial institution may not cost so much. These considerations may also affect the choice between debt and equity and hence the capital structure.
(i) Risk Consideration: Use of debt increases the financial risk of a business. Financial risk refers to a position when a company is unable to meet its fixed financial charges namely interest payment, preference dividend and repayment obligations. Apart from the financial risk, every business has some operating risk (also called business risk). Business risk depends upon fixed operating costs. Higher fixed operating costs result in higher business risk and vice-versa. The total risk depends upon both the business risk and the financial risk. If a firm’s business risk is lower, its capacity to use debt is higher and viceversa.
(j) Flexibility: If a firm uses its debt potential to the fullest, it loses flexibility to issue further debt. To maintain flexibility, it must maintain some borrowing power to take care of unforeseen circumstances.
(k) Control: Debt normally does not cause a dilution of control. A public issue of equity may reduce the management holding in the company and makes it vulnerable to takeover. This factor also influences the choice between debt and equity especially in companies in which the current holding of management is on a lower side.
(l) Regulatory Framework: Every company operates within a regulatory framework provided by the law e.g.; public issue of shares and debentures have to be made under SEBI guidelines. Raising funds from banks and other financial institutions requires fulfillment of other norms. The relative ease with which these norms can be met or the procedures completed may also have a bearing upon the choice of the source of finance.
(m) Stock Market Conditions: If the stock markets are bullish, equity shares are more easily sold even at a higher price. Use of equity is often preferred by companies in such a situation. However, during a bearish phase, a company may find raising of equity capital more difficult and it may opt for debt. Thus, stock market conditions often affect the choice between the two.
(n) Capital Structure of other Companies: A useful guideline in the capital structure planning is the debt equity ratios of other companies in the same industry. There are usually some industry norms which may help. Care however must be taken that the company does not follow the industry norms blindly. For example, if the business risk of a firm is higher, it cannot afford the same financial risk. It should go in for low debt. Thus, the management must know what the industry norms are, whether they are following them or deviating from them and adequate justification must be there in both cases.
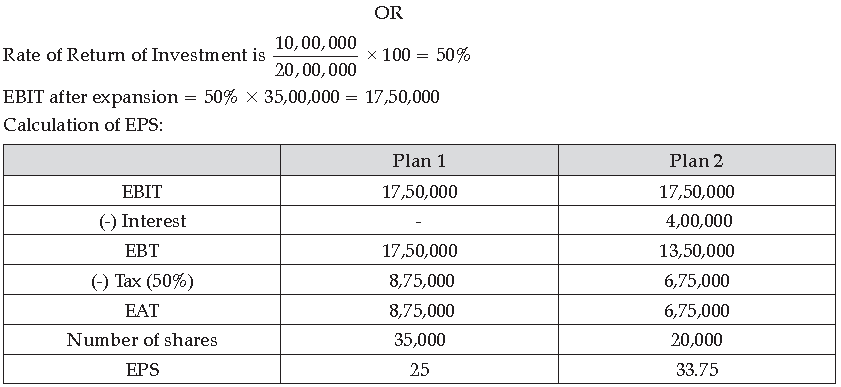
The company should use Plan 2 in order to increase the return to the equity shareholders.
