VBQs Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Short Answer Type Questions
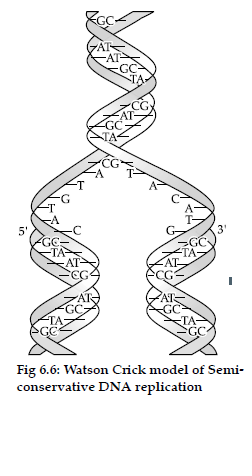
Question. Describe the experiment that helped demonstrate the semi-conservative mode of DNA Replication.
Answer : Grown E.coli in 15NH4Cl for many generations to get 15N incorporated into DNA, then the cells were transferred into 14NH4Cl , The extracted DNA was centrifuged in CsCl and measured to get their densities, DNA extracted from the culture after one generation (20 minutes), showed intermediate hybrid density, DNA extracted after two generations (40 minutes) showed light DNA and hybrid DNA.

A correctly labelled diagrammatic representation in lieu of the above explanation of experiment to be considered.
Detailed Answer :
Meselson and Stahl experiment :
(i) They used the bacterium E. coli with the technique of density gradient centrifugation, which
separates molecules on the basis of their density.
(ii) They cultured E. coli in a medium containing heavy isotope of N15 as the sole nitrogen source.
This led to the incorporation of N15 into the newly synthesized DNA, which ultimately made the DNA heavy.
(iii) This heavy DNA was separated from the normal DNA by density gradient centrifugation using cesium chloride as the gradient.
(iv) The cells were then transferred into the medium with N14 as the nitrogen source. Samples were taken from this medium and the DNA was extracted.
Observation : Since, E.coli divides every 20 minutes, the DNA extracted after 20 minutes i.e. after first generation in the experiment had a hybrid density i.e. it was intermediate between N14 and N15 type of DNA.
The DNA extracted after 40 minutes i.e. after second generation had equal amounts of hybrid and light densities.
Conclusion : This implies that in newly synthesized DNA one of its strands is old (N15 type) and the other strand is new (N14 type).
Thus, replication is semi-conservative.
Question. (i) A DNA segment has a total of 2,000 nucleotides, out of which 520 are adenine containing nucleotides. How many purine bases this DNA segment possesses ?
(ii) Draw a diagrammatic sketch of a portion of DNA segment to support your answer.
Answer : (i) Number of Nucleotides = 2000
Number of Adenine (A-purine) containing
nucleotides = 520
According to Chargaff’s rule Purine pairs with pyrimidine, thus ‘A’ pairs with ‘T’ and ‘G’ pairs with ‘C’.
∴ Number of Thymine (T-pyrimidine) nucleotides = 520
∴ Total number of A + T = 520+520 = 1040
∴ Number of G + C nucleotides = 2000 – 1040 = 960
∴ Number of guanine nucleotides = 960/2 = 480
∴ Number of purine bases (A + G) = 520 + 480 = 1000
(ii) For diagrammatic sketch of DNA segment,
Question. Why is DNA molecule considered as a better hereditary material than RNA molecule ?
OR
Why is DNA a better genetic material when compared to RNA ?
Answer : DNA molecule is a better hereditary material as:
(i) It is more stable (due to presence of thymine and not uracil as in RNA).
(ii) Less reactive than RNA (as RNA has 2’ – OH making it more reactive).
(iii) Being less reactive , DNA is not easily degradable (RNA being more reactive is easily degradable).
(iv) Rate of mutation is slow (Rate of mutation in RNA is faster).
Question. (i) Given below is a single stranded DNA molecule. Frame and label its sense and antisense RNA molecule.
5’ ATGGGGCTC 3’ sense
(ii) How the RNA molecules made from above DNA strand help in silencing of the specific RNA molecules ?
Answer : (i) 5’ ATGGGGCTC 3’ sense
3’ TACCCCGAG 5’ antisense
RNA 5’ AUGGGGCUC 3’ sense
3’ UACCCCGAG 5’ antisense
(ii) The two strands of RNA (i.e. sense and antisense) being complementary will bind with each other and form double stranded RNA. As a result its translation and protein expression would be inhibited.
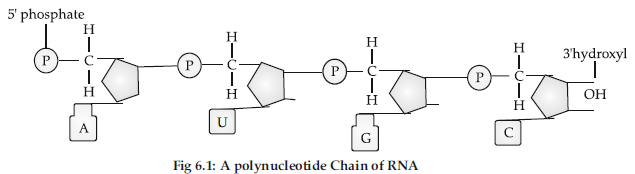
Question. Describe the structure of an RNA polynucleotide chain having four different types of nucleotides.
Answer : (i) RNA is a single-chain poly-ribonucleotide that works as a carrier of coded genetic or hereditary information from DNA to cytoplasm by taking part in protein synthesis.
(ii) It contains 70–12000 four different types of ribonucleotides or ribotides joined end to end.
(iii) The axis or backbone is formed of alternate residues of phosphate and ribose sugars.
(iv) The phosphate combines with carbon 5’ of its sugar and carbon 3’ of the next sugar.
(v) Nitrogen bases are attached to sugars at carbon 1’ of the latter.
(vi) There are 4 bases : Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C).
Figure representing polynuceotide chain of RNA:
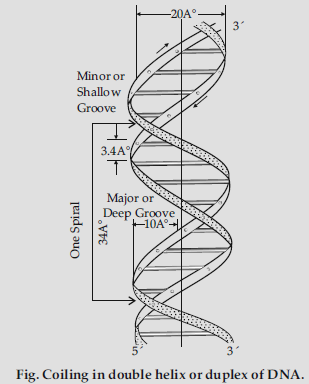
Question. List the salient features of double helix structure of DNA.
Answer : DNA helix is made up of two polynucleotide chains, each constituted by sugar-phosphatebases, the chains are antiparallel in polarity (5’ → 3’ and 3’ → 5’), the bases are linked with H-bonds, Adenine pair with Thymine with two H-bonds while Guanine pair with Cytosine with three H-bonds, Coiling of the chain are in right handed fashion, pitch of the helix is 3.4 nm and there are 10 bp per turn, the plane of one base pair stack over the other in a double helix.
Question. (i) Construct a complete transcription unit with promotor and terminator on the basis of the hypothetical template strand given below :
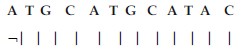
(ii) Write the RNA strand transcribed from the above transcription unit along with its polarity.
Answer :

Question. (i) Why did Meselson and Stahl used 14N and 15N isotopes as the sources of nitrogen present in the culture medium in their experiment ? Explain.
(ii) Write the conclusion drawn by them from the experiment.
Answer : (i) Meselson and Stahl used 14N and 15N isotopes as the sources of nitrogen present in the culture medium in their experiment as nitrogen is a major constituent of DNA. Moreover 15N is by far the most abundant isotope of nitrogen and DNA with the heavier 15N isotope is also functional. E.coli can be grown for several generations in a medium with 15N easily. When DNA is extracted from these cells and centrifuged on a salt density gradient, the DNA separates out at the point at which its density equals that of the salt solution.
(ii) The experiment proves the semi-conservative nature of replication of DNA. In this type of replication, one strand of daughter DNA is new and one strand is old. It means, one strand of daughter duplex is derived from the old DNA, while the other strand is formed new. It proves semi-conservative replication of DNA.
Question. (i) Name the enzyme that catalyses the transcription of hnRNA.
(ii) Why does the hnRNA need to undergo changes ?
List the changes hnRNA undergoes and where in the cell such changes take place.
Answer : (i) RNA polymerase II.
(ii) Has (non-functional) introns.
(Methyl guanosine tri-phosphate is added to 5’ end) capping, tailing (Poly A tail at 3’ end added), splicing (introns are removed and exons are joined).
Nucleus.
Detailed Answer :
(i) The enzyme RNA polymerase II catalyses the transcription of hnRNA.
(ii) The hnRNA in eukaryotes needs to undergo changes for converting it into functional RNA. The hnRNA contain both exons and introns. The exons are functional coding segments while introns are non functional and non coding sequences. This hnRNA undergo processing where the introns are removed and exons are joined by a process called splicing. Now this transcribed heterogenous nuclear RNA undergoes additional processing called capping and tailing. In capping methyl guanosine triose phosphate is added to 5′ end and in tailing 200-300 adenylate residues are added at 3’ end of spliced RNA. This is completely processed hnRNA. This is now called a mRNA. Such changes of processing takes place in the nucleus of the cell.
Question.

Why do you see two different types of replicating strands in the given DNA replication fork ?
Explain. Name these strands.
Answer : (i) In long DNA molecules, since the two strands of DNA cannot be separated in its entire length, the replication occur within a small opening to the DNA helix, referred to as a replication fork.
(ii) The DNA-dependent DNA polymerases catalyse polymerization of the nucleotides only in 5’ → 3’ direction.
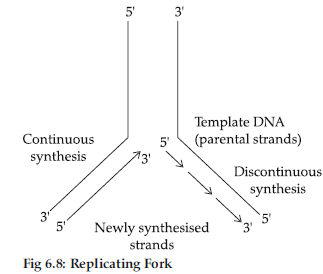
Consequently, on one of the template strands (with 3’ → 5’ polarity) the synthesis of DNA is continuous, while on the other template strand (with polarity 5’ → 3’), the synthesis of DNA is discontinuous i.e. short stretches of DNA are synthesized.
(iii) The discontinuously synthesized strands are later joined together by the enzyme DNA ligase.
Question. (i) Draw a labelled schematic diagram of a replication fork showing continuous and discontinuous replication of DNA strands.
(ii) State a reason why is the replication continuous and discontinuous in the diagram drawn.
Answer : (i)

(ii) 2 strands are antiparallel, DNA polymerase acts only in one direction i.e. 5′ → 3′
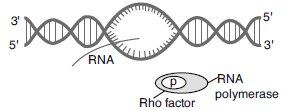
Question. Describe the termination process of transcription in bacteria.
Answer : (i) RNA polymerase binds to the promotor and initiates transcription. It uses nucleotide triphosphates as substrates and polymerises in a template dependent fashion following the rule of complementary. It somehow also facilitates opening of the helix structure and continues elongation.
Only a short stretch of RNA remains bound to the enzyme. Once the polymerase reaches the terminator region, the nascent RNA falls off, also the RNA polymerase. This results into termination of the transcription.
(ii) RNA polymerase associates transiently with termination factor (rho) to terminate the transcription. Association of this factor alters the specificity of the RNA polymerase to terminate.
Question. (a) Mention two events in which DNA is unzipped.
(b) Predict the consequences when both the template and the coding strands of a DNA segment participate in transcription process?
Answer : (a) Replication and Transcription.
(b) If both the stands take part in transcription,
(i) One segment of DNA would be coding for two different proteins which will complicate the genetic information machinery
(ii) Two RNA molecules will be produced, complementary to each other, hence form a double stranded RNA, translation would not be possible.
Question. Explain the post transcriptional modifications the hn-RNA undergoes in eukaryotic cell.
Answer : ♦ Splicing , Introns are removed and exons are joined.
♦ Capping, Methyl guanosine triphosphate / mGPPP is added to the 5’ end of hnRNA.
♦ Tailing, Polyadenylate residues are added to 3’-end in a template independent manner.
Question. If the base adenine constitute 30% of an isolated DNA fragment, then what is the expected percentage of the base cytosine in it.
Answer : As A = 30%
T = 30% (as A = T)
A + T = 60%
G + C = 100 – 60 = 40%
C (Cytosine) =20% (as C = G)
Question. (i) If the sequence of the coding strand intranscription unit is written as follows :
5’—ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCAT
G—3’
write down the sequence of mRNA.
(ii) How is repetitive/satellite DNA separated from bulk genomic DNA for various genetic experiments.
(iii) Mention the polarity of DNA strands a-b & c-d shown in the replicating fork given below :
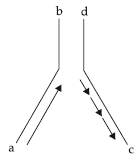
Answer : (i) 5’—AUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUG —3′
(ii) By density gradient centrifugation.
(iii) Polarity of DNA strand a–b is 3’→5′ & c–d has polarity 5’→3′. 1 × 3 = 3
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Answer the following questions based on Hershey and Chase experiments :
(i) Name the kind of virus they worked with and why ?
(ii) Why did they use two types of culture media to grow viruses in ? Explain.
(iii) What was the need for using a blender and later a centrifuge during their experiments ?
(iv) State the conclusion drawn by them after the experiments.
Answer : (i) Bacteriophage, they infect bacteria.
(ii) Two types of culture media were used in order to make protein of viruses (with the help of S35)
radioactive in one case, and DNA molecule in virus (with the help of P32 radioactive in other case.
so as to identify which one of the two had entered into the bacteria during viral infection.
(iii) Blender : To separate the viral protein coats that are still attached to the surface of bacteria.
Centrifuge : To separate lighter supernatant (containing viral protein coats) from denser residue (containing bacteria).
(iv) DNA is the genetic material i.e. passed from virus to bacteria.
Detailed Answer :
(i) Hershey & Chase carried out experiments with viruses which infect bacteria. Such viruses are called bacteriophage. While infecting bacteria the protein capsid or coat remains outside on the bacterial wall and its genetic material (DNA) enters the bacterial cell which treats the bacterial DNA as its own to synthesize the viral particle inside the bacterial cell.
(ii) They used two separate culture media for growing these bacteriophages, one culture medium containing radioactive phosphorus (P32) and the other containing radioactive sulphur (S35). The bacteriophages were then cultured on these two types of media separately.
The viruses cultured in a medium enriched with radioactive phosphorus, was found to contain radioactive DNA but not radioactive protein because phosphorus is a component of DNA and not of protein. Similarly, the bacteriophages grown in the medium enriched with radioactive sulphur contained radioactive protein and not radioactive DNA because sulphur is a component of some amino acids forming proteins of capsids of viruses.
(iii) The blender was used to remove the proteinaceous capsids of virus which were attached with the bacterial cell wall. The bacteria infected with virus (bacteriophages) were agitated in the blender for separating viral coats from bacteria. Centrifugation later was done which resulted in the formation of a supernatant containing viral capsids and the bacteria got sedimented at the bottom.
(iv) Hershey & Chase concluded after the experiment that the genetic material that is passed from virus to the bacteria is not the protein coat but DNA. It proves the DNA is the genetic material and not the protein.
Question. Describe the packaging of DNA helix in a prokaryotic cell and an eukaryotic nucleus.
Answer : Prokaryotes : Negatively charged DNA is held with positively charged proteins in nucleoid, DNA in nucleoid is organised in large loops held by protein.
Eukaryotes : In nucleus, the negatively charged DNA is wrapped around positively charged histone octomer to form nucleosome, nucleosomes are repeated to constitute chromatin at higher level, additional set of non-histone chromosomal protein gets associated with chromatin.
Detailed Answer:
Packaging of DNA helix in prokaryotes : In prokaryotes, there is no true nucleus. The DNA is present in a region called nucleoid. The DNA which is negatively charged is held with some positively charged non-histones basic proteins. DNA in nucleoid is organized in large loops held by protein.
DNA Packaging in eukaryotes : In eukaryotes, there is true nucleus. Chromosomes are made up of DNA and histone proteins. The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around positively charged histone octamer (2 molecules each of H2A, H2B, H3 & H4) to form nucleosome which form the repeating units of chromatin. Nucleosomes are further coiled and packed to form solenoids. Further, super coiling forms chromatin fibers and then chromatids. They further coils and condenses at metaphase stage of cell division to form chromosomes.
Question. (a) Why does DNA replication occur in small replication forks and not in its entire length ?
(b) Why is DNA replication continuous and discontinuous in a replication fork ?
(c) State the importance of origin of replication in a replication fork.
Answer : (a) DNA being very long , requires high energy for opening along its entire length.
(b) DNA dependent DNA polymerase catalyse polymerisation only in one direction i.e. 5’ 3’.
Two strands of DNA are anti parallel and have opposite polarity.
(c) Site where replication originates.
Question. (i) What is Central dogma ? Who proposed it ?
(ii) Describe Meselson and Stahl’s experiment to prove that the DNA replication is semi-conservative.
Answer : (i) Central dogma :

Given by Francis Crick.
(ii) Meselson and Stahl experiment :

(Same value points to be awarded in an explanation)
Detailed Answer :
(i) Central Dogma : The principle of central dogma of molecular biology was proposed by Francis Crick. This states that the genetic information always flows unidirectionally from DNA to mRNA (Transcription) and then from mRNA to protein or (polypeptide translation).
Question. (i) Hershey and Chase carried their experiment in three steps : infection, blending, centrifugation. Explain each step.
(ii) Write the conclusion and interpretation of the result they obtained.
OR
Describe the Hershey and Chase experiment.
Write the conclusion drawn by the scientists after their experiment.
OR
How did Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase arrive at the conclusion that DNA is the genetic material ?
Answer : (i) Infection : Radioactive phosphorus / phosphorus labelled bacteriophages were allowed to infect E.coli – growing in a culture medium, simultaneously radioactive sulphur / Sulphur labelled bacteriophage was allowed to infect E.coli growing in another culture medium.
(a) Blending : As infection proceeds – the viral coats are removed from the bacteria by agitating in a blender.
(b) Centrifugation : virus particles were separated from bacteria by spinning them in a centrifuge.
(ii) Conclusion : DNA is the genetic material.
Interpretation : Sulphur labelled viral protein did not enter the bacteria during infection, whereas phosphorus labelled viral DNA entered into the bacteria to cause infection.
Detailed Answer :
Infection :
(i) Hershey and Chase made two preparation of bacteriophage – In one, proteins were labeled with S35 by putting in medium containing radioactive sulphur (S35). In the second, DNA was labeled with P32 by putting in a medium containing radioactive phosphorus (P32).
(ii) These preparations were used separately to infect E.coli.
Blending :
(i) After infection, the E.coli cells were gently agitated in a blender to separate the phage particles from the bacteria.
Centrifugation :
(i) Then the culture was centrifuged. Heavier bacterial cells were formed as a pellet at the bottom. Lighter viral components outside the bacterial cells remained in the supernatant.
(ii) They found that,
(a) Supernatant contains viral protein labelled with S35 i.e. the viral protein had not entered the bacterial cells.
(b) The bacterial pellet contains radioactive P. This showed that viral DNA labelled with P32 had entered the bacterial cells. This proves that DNA is the genetic material.

Question. (a) State the ‘Central dogma’ as proposed by Francis Crick. Are there any exceptions to it ? Support your answer with a reason and an example.
(b) Explain how the biochemical characterisation (nature) of “Transforming Principle” was determined, which was not defined from Griffith’s experiments.
Answer : (b) Protein, DNA and RNA were purified from heat killed S strain / smooth Streptococcus pneumonia = ½
Protein + Protease → transformation occurred (R cell to S type) = ½
RNA + RNA ase → transformation occurred (R cell to S type) = ½
DNA + DNA ase → transformation inhibited = ½
Hence DNA alone is the transforming material = ½
Detailed Answer:
(a) Central dogma proposed by Francis Crick states that the genetic information flows from DNA to RNA through transcription and from RNA to proteins through translation.

Yes, there are some exceptions to this process. In some viruses, the genetic material is in the form of RNA. In such cases, the direction of genetic information flow is reversed. The RNA is first converted into DNA through the process of reverse transcription. The DNA thus formed follows the usual path of central dogma i.e. it is first transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into proteins.
An example of organism exhibiting reverse transcription is Influenza A virus.
(b) Biochemical characterization of transforming principle was discovered by Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod and Maclyn McCarty
♦ They worked to determine the biochemical nature of ‘transforming principle’ in Griffith’s experiment.
♦ They purified biochemicals (proteins, DNA, RNA etc.) from the heat killed S cells to see which one could transform live R cell into S cells.
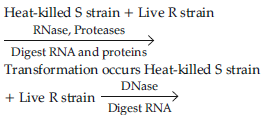
Transformation does not occur and mouse survives.
They discovered that :
♦ DNA alone is transformed.
♦ Proteases and RNases did not affect transformation.
♦ Digestion with DNase inhibited transformation, suggesting that the DNA caused the transformation.
Thus, they concluded that DNA is the hereditary material.
