MCQs for Mathematics Class 11 with Answers Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities
Students of class 11 Mathematics should refer to MCQ Questions Class 11 Mathematics Linear Inequalities with answers provided here which is an important chapter in Class 11 Mathematics NCERT textbook. These MCQ for Class 11 Mathematics with Answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and examination guidelines for Class 11 Mathematics. The following MCQs can help you to practice and get better marks in the upcoming class 11 Mathematics examination
Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities MCQ with Answers Class 11 Mathematics
MCQ Questions Class 11 Mathematics Linear Inequalities with answers provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of grade 11. These objective questions with solutions are expected to come in the upcoming Standard 11 examinations. Learn the below provided MCQ questions to get better marks in examinations.
Question. The cost and revenue functions of a product are given by C(x) = 20x + 4000 and R(x) = 60x + 2000, respectively, where x is the number of items produced and sold. How many items must be sold to realise some profit?
(a) Less than 40
(b) More than 50
(c) Less than 50
(d) Exactly 50
Answer
B
Question: The quadratic equations x2-6x+a=0 and x2-cx+6=0 have one root in common. The other roots of the first and second equations are integers in the ratio 4 3: . Then, the common root is
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer
A
Question: If α and β are the roots of the equation x2-x+1=0, then a 2009+ β2009 is equal to
(a) -2
(b) -1
(c) 1
(d) 2
Answer
C
Question: If the equations x2+2x+3=0 and ax2+bx+c=0, a,bc∈R,Î have a common root, then a: b: c is
(a) 1 : 2 : 3
(b) 3 : 2 : 1
(c) 1 : 3 : 2
(d) 3 : 1 : 2
Answer
A
Question: If the roots of the equation bx2+cx+a=0 be imaginary, then for all real values of x, the expression 3b2x2+6bcx+2c2
(a) greater than 4ab
(b) less than 4ab
(c) greater than -4ab
(d) less than -4ab
Answer
C
Question: If the roots of the quadratic equation x2+px+q=0 are tan 30° and tan 15°, then the value of 2+q-p is
(a) 3
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) 2
Answer
A
Question: All the values of m for which both roots of the equation x2-2mx+m2-1=0 are greater than -2
but less than 4 lie in the interval
(a) m > 3
(b) -1 <m<3
(c) 1 < m<4
(d) – 2<m<0
Answer
B
Question: If the difference between the roots of the equation x2+ax+1=0 is less than √5, then the set of possible values of a is
(a) (-3 3,)
(b) (-3,∞)
(c) (3,∞)
(d) (-∞,-3)
Answer
A
Question: The value of a for which the sum of the squares of the roots of the equation x2-(a-2)x-a-1=0 the least value is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 0
(d) 1
Answer
D
Question: If the cube roots of unity are 1,ω and ω2,, then the roots of the equation (x -1)3+8=0, are
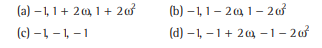
Answer
B
Question: If both the roots of the quadratic equation x2-2kx+k2-5=0 are less than 5, than k lies in the interval
(a) [4, 5]
(b) (-∞,4)
(c) (6 ,∞)
(d) (5, 6]
Answer
B
Question: If the roots of the equation x2-bx+c=0 be two consecutive integers, then b2-4c equals
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) -2
Answer
A
Question:
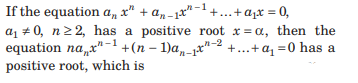
(a) equal to α
(b) greater than or equal to α
(c) smaller than α
(d) greater than α
Answer
C
Question: If one root of the equation x2+px+12=0 is 4, while the equation x2+ px+q=0 has equal roots, then the value of q is
(a) 49/4
(b) 12
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
A
Question: If (1 – p) is a root of quadratic equation x2+px+(1-p)=0,then its roots are
(a) 0, 1
(b) – 1, 1
(c) 0, -1
(d) – 1, 2
Answer
C
Question: If the sum of the roots of the quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0 is equal to the sum of the squares of their reciprocals, then a/c, b/a, and c/b are in
(a) arithmetic progression
(b) geometric progression
(c) harmonic progression
(d) arithmetico-geometric progression
Answer
C
Question: Let two numbers have arithmetic mean 9 and geometric mean 4. Then, these numbers are the roots of the quadratic equation
(a) x2+18x+16=0
(b) x2-18x+16=0
(c) x2+18x-16=0
(d) x2-18x-16=0
Answer
B
Question: The value of a for which one root of the quadratic equation (a2-5a+3) x2+3a-1)x+2 is twice as large as the other, is
(a) 2/3
(b) -2/3
(c) 1/3
(d) -1/3
Answer
A
Question:

Answer
B
Question: The number of the real solutions of the equation x2-3|x|+2=0 is
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 3
Answer
B
Question. If 3x – 7 < 5 + x, 11 – 5 x ≤ 1, then x ∈
(a) [2, 6]
(b) [–2, 6]
(c) [2, 6)
(d) (–2, 6)
Answer
C
Question. If 7x + 3 < 5x + 9 then x ∈
(a) (–∞, 3]
(b) (–∞, ∞)
(c) (–∞, 3)
(d) [3, ∞)
Answer
C
Question. If −5 ≤ 5 – 3x/2 ≤ 8, then x ∈
(a) [-11/3 , 5]
(b) [–5, 5]
(c) [-11/3, ∞]
(d) (– ∞, ∞)
Answer
A
Question. If 1 ≤ |x –2| ≤ 3, then x ∈
(a) [–1, 5]
(b) [–1, 1] ∪ [3, 5]
(c) (–1, 0) ∪ (2, 5)
(d) (–1, 5)
Answer
B
Question. Solution of |x2 – 10| ≤ 6 is
(a) (2, 4)
(b) (– 4, – 2)
(c) (– 4, – 2) ∪ (2, 4)
(d) [– 4, – 2] ∪ [2, 4]
Answer
D
Question. If |2x – 3| < |x + 5|, then x belongs to
(a) (–3, 5)
(b) (5, 9)
(c) (-2/3 ,8)
(d) (-8, 2/3)
Answer
C
Question. (i) x ≥ 2

(ii) y ≥ 3
(iii) 5x + 4y ≤ 40
(iv) 8x + 3y ≤ 10
(v) x ≤ 0
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) only (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (v)
Answer
B
Question. If the expression (mx – 1 + 1/x) is always nonnegative, then the minimum value of m must be
(a) -1/2
(b) 0
(c) 1/4
(d) 1/2
Answer
C
Question. Solution of l1 + 3/xl > 2 is
(a) (0, 3]
(b) [–1, 0)
(c) (–1, 0) ∪ (0, 3)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. If (x – 1)(x2 – 5x + 7) < (x – 1), then x belongs to
(a) (1, 2) ∪ (3, ∞)
(b) (2, 3)
(c) (–∞, 1) ∪ (2, 3)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. If 4x + 3 < 6x + 7, then x ∈
(a) (2, ∞)
(b) (–2, ∞)
(c) (–∞, 2)
(d) (– ∞, ∞)
Answer
B
Question. If |x + 2| ≤ 9, then
(a) x ∈(–7, 11)
(b) x ∈[–11, 7]
(c) x ∈(– ∞, –7) ∪ (11, ∞)
(d) x ∈(– ∞, –7) ∪ [11, ∞)
Answer
B
Question. The inequality representing the following graph is:

(a) |x| < 5
(b) |x| ≤ 5
(c) |x| > 5
(d) |x| ≥ 5
Answer
A
Question. If x – 2/x + 5 > 2 , then x ∈
(a) (–12, 5)
(b) (–12, –5)
(c) (–5, 12)
(d) (5, 12)
Answer
B
Question. Solution of (x – 1)2(x + 4) < 0 is
(a) (– ∞, 1)
(b) (–∞, –4)
(c) (– 1, 4)
(d) (1, 4)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) If x > y and b < 0, then bx < by
(b) If x > y, then x > 0 and y < 0
(c) If xy < 0, then x > 0 and y > 0
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. (i) x + 2y ≤ 8

(ii) x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
(iii) x ≤ 0, y ≤ 0
(iv) 2x + y ≤ 8
(v) 4x + 5y ≥ 40
(a) (i), (iii) and (v)
(b) (i), (iv) and (v)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. Solution of | 3x + 2 | < 1 is
(a) [-1, -1/3]
(b) {-1/3 , -1}
(c) (-1, – 1/3)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Solution of |x+ 1/x | > 2 is
(a) R – {0}
(b) R – {–1, 0, 1}
(c) R – {1}
(d) R – {–1, 1}
Answer
B
Question. The marks obtained by a student of Class XI in first and second terminal examination are 62 and 48, respectively. Find the minimum marks he should get in the annual examination to have an average of at least 60 marks.
(a) 50
(b) 60
(c) 70
(d) 80
Answer
C
Question. The length of a rectangle is three times the breadth. If the minimum perimeter of the rectangle is 160 cm, then
(a) breadth > 20 cm
(b) length < 20 cm
(c) breadth ≥ 20 cm
(d) length ≤ 20 cm
Answer
C
Question. Solution of |3 – x| = 3 – x is
(a) x < 3
(b) x > 3
(c) x ≥ 3
(d) x ≤ 3
Answer
D
Question. Solution of 2x – 1 = | x + 7| is
(a) – 2
(b) 8
(c) – 2, 8
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Solution of 2x-3/3x – 5 ≥ 3 is
(a) [1,12/7]
(b) (5/3 , 12/7]
(c) (–∞ , 5/3)
(d) [2/7, ∞)
Answer
B
Question. Solution of |x+ 1/x | < 4 is
(a) (2 − 3, 2 + 3)∪(−2 − 3,− 2 + 3)
(b) R − (2 − 3, 2 + 3)
(c) R − (−2 − 3, − 2 + 3)
(d) none of these
Answer
A
Question. Solution of |x – 1| ≥ | x – 3| is
(a) x ≤ 2
(b) x ≥ 2
(c) [1, 3]
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The set of values of x which satisfy the inequations 5x + 2 < 3x + 8 and x + 2/x – 1 < 4 is
(a) (– ∞, 1)
(b) (2, 3)
(c) (– ∞, 3)
(d) (– ∞, 1) ∪ (2, 3)
Answer
D
Question. Solution of 0 < |3x + 1| < 1/3 is
(a) (-4/9 , 2/9)
(b) [-4/9 , -2/9]
(c) (-4/9 , -2/9) – {-1/3}
(d) [-4/9 , -2/9] – {-1/3}
Answer
C
Question. Find all pairs of consecutive odd natural numbers, both of which are larger than 10, such that their sum is less than 40.
(a) (11, 13), (13, 15), (15, 17), (17, 19)
(b) (11, 13), (13, 15), (15, 17)
(c) (21, 23), (23, 25), (25, 27), (27, 29)
(d) (15, 17), (17, 19), (19, 21), (21, 23)
Answer
A
Question. Solutions of the inequalities comprising a system in variable x are represented on number lines as given below, then 36
(a) x ∈(– ∞, –4] ∪ [3, ∞)
(b) x ∈ [–3, 1]
(c) x ∈(– ∞, –4) ∪ [3, ∞)
(d) x ∈ [–4, 3]
Answer
B
Question. If –3x + 17 < –13, then
(a) x ∈ (10, ∞)
(b) x ∈ [10, ∞)
(c) x ∈ (–∞, 10)
(d) x ∈ [–10, 10)
Answer
A
Question. If |x + 3| ≥10, then
(a) x ∈(–13, 7]
(b) x ∈(–13, 7)
(c) x ∈(– ∞, –13] ∪ [7, ∞)
(d) x ∈(– ∞, –13) ∪[7, ∞)
Answer
C
Question. Solution of x – 7/x +3 > 2 is
(a) (– 3, ∞)
(b) (– ∞, –13)
(c) (– 13, –3)
(d) (– 13, 3)
Answer
C
Question. If lx -2 l/x – 2 ≥ 0 then x ∈
(a) [2, ∞)
(b) (2, ∞)
(c) (–∞, 2)
(d) (–∞, 2]
Answer
B
Question. x and b are real numbers. If b > 0 and |x| > b, then
(a) x ∈(–b, ∞)
(b) x ∈(– ∞, b)
(c) x ∈(–b, b)
(d) x ∈(– ∞, –b) ∪ (b, ∞)
Answer
D
Question. If |3 – 4x| ≥ 9, then x ∈
(a) (–∞, –3) ∪ (3, ∞)
(b) (−∞ , -3/2] ∪ (3 , ∞)
(c) (−∞ ,-3/2] ∪ (0 , ∞)
(d) (−∞ ,-3/2] ∪ [3 , ∞)
Answer
D
Question. The inequality 2/x < 3 is true, when x belongs to
(a) [2/3 , ∞)
(b) (–∞ , 2/3)
(c) (–∞ ,0) ∪(2/3,∞)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. If |x – 1| > 5, then
(a) x ∈(–4, 6)
(b) x ∈[–4, 6]
(c) x ∈(– ∞, –4) ∪ (6, ∞)
(d) x ∈(– ∞, –4) ∪ [6, ∞)
Answer
C
Question. If –8 ≤ 5x – 3 < 7, then x ∈
(a) (–1, 2)
(b) [–1, 2)
(c) [–2, ∞)
(d) [–2, 0)
Answer
B
Assertion & Reasoning Based
(a) Assertion and Reason both are correct statements and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason both are correct statements but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but Reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but Reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : If –5 ≤ 2x + 9 ≤ 2, then x ∈ [–7, –3.5].
Reason : The graphical representation of –5 ≤ 2x + 9 ≤ 2 is
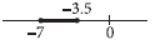
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : |3x – 5| > 9 ⇒ x∈ (– ∞ , -4/3)∪ (14/3 , ∞) .
Reason : The region containing all the solutions of an inequality is called the solution region.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : If 11x – 9 ≤ 68, then x ∈ (–∞, 7).
Reason : If an inequality consist of signs ≤ or ≥, then the point on the line are also included in the solution region.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : If x ≥ – 3, then x + 5 ≥ 2.
Reason : Same number can be added to both sides of the inequality without changing the sign of inequality.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : If a < b, c < 0, then a/c < b/c .
Reason : If both sides are divided by the same negative quantity, then the inequality is reversed.
Answer
D
We hope the above MCQ Questions Class 11 Mathematics Linear Inequalities with answers based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS are really useful for you. Linear Inequalities is an important chapter in Class 11 as it provides very strong understanding about this topic. Students should go through the answers provided for the MCQs after they have themselves solved the questions. All MCQs have been provided with four options for the students to solve. These questions are really useful for benefit of class 11 students. Please go through these and let us know if you have any feedback in the comments section.
