Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 12 Chemistry teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 12th.
Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids are very important and should be revised daily.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
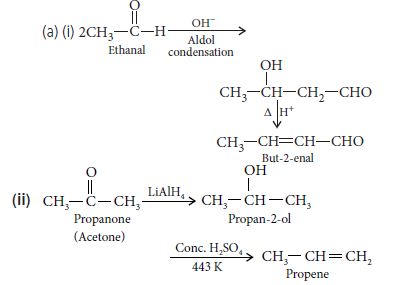
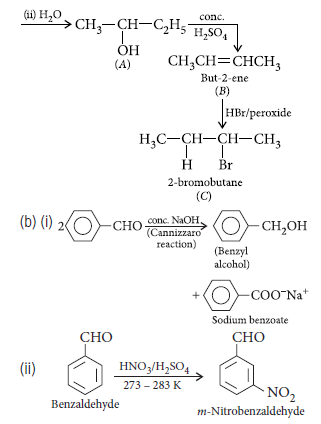
Question. Write structures of compounds A and B in each of the following reactions :

Answer.
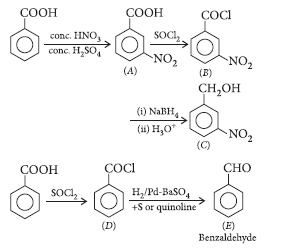
Question. Write structures of compounds A and B in each of the following reactions.
Answer.

Question. Complete the following reactions :

Answer.
Question. Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points.
CH3CHO, CH3COOH, CH3CH2OH
Answer.Increasing order of boiling point :
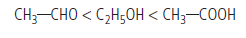
Question. Give reasons :
Chloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic acid.
Answer.Chloroacetic acid has lower pKa value than acetic acid; ‘Cl’ in chloroacetic acid shows –I effect, it creates less electron density on oxygen of carboxylic acid. Thus, release of proton becomes easier. In case of acetic acid, the state of affair is just opposite. Hence, chloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic acid.
Question. Write the equation involved in Etard reaction.
Answer.Etard reaction :
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the following :
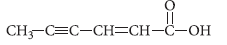
Answer.Hex-2-en-4-yn-oic acid
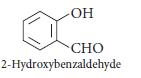
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the following compound :
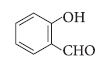
Answer.
Question. Write chemical equations for the following reactions :
Benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated in presence of Pd/BaSO4.
Answer.
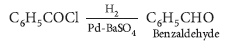
Question. Aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling points than corresponding alcohols. Why?
Answer.The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower than that of corresponding alcohols and acids due to absence of intermolecular H–bonding in aldehydes and ketones.
Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question. (i) What is the advantage of using DIBAL-H as reducing agent?
(ii) Which of the following can be nitrated more easily and why? Benzoic acid or phenol.
Answer.(i) DIBAL–H reduces alkynes to alkenes but does not reduce ethylenic double bonds and hence this reagent can be used to reduce unsaturated nitriles to the corresponding unsaturated aldehydes.
(ii) Phenol gets easily nitrated than benzoic acid. Because carboxyl group is ring deactivating group whereas hydroxyl group is ring activating group.
Question. Give reasons :
(i) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta-position.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give the characteristic reactions of carbonyl group.
Answer.(i) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta-position. Due to resonance in benzoic acid, there is high electron density at meta-position. Therefore, electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta-position.
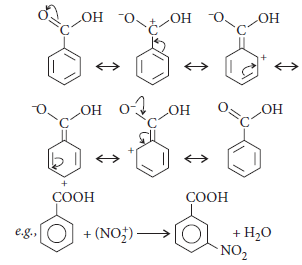
(ii) The carbonyl group in —COOH is inert and does not show nucleophilic addition reaction like carbonyl compound.It is due to resonance stabilisation of carboxylate ion :
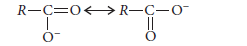
Question. A compound having the molecular formula C3H6O forms a crystalline white ppt. with sodium bisulphite and reduces Fehling’s solution. Suggest the structural formula and IUPAC name of this compound. Name an isomer for it from a group other than its own.
Answer.Since the compound forms crystalline white precipitate with sodium bisulphite, it contains a carbonyl group. The compound reduces Fehling’s solution so, the carbonyl group is an aldehyde.*
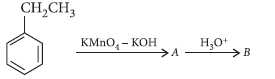
Question. Describe how the following conversions can be brought about :
(i) Ethylbenzene to benzoic acid
(ii) Bromobenzene to benzoic acid
Answer.

Question. A compound ‘A’ of molecular formula C2H3OCl undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structure of A, B, C and D in the following reactions :

Answer.

Question. Account for the following :
(i) CH3CHO is more reactive than CH3COCH3 towards reaction with HCN.
(ii) There are two –NH2 groups in semicarbazide (H2NNHCONH2).
However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazone.
Answer.(i) It is a nucleophilic addition reaction, in which CN – acts as a nucleophile. CH3CHO undergoes nucleophilic addition reactions faster than CH3COCH3 as in CH3COCH3
there are two electron releasing methyl groups attached to the carbonyl carbon that hinders the approach of nucleophile to carbonyl carbon and reduce the electrophilicity of the
carbonyl group while in CH3CHO, there is only one methyl group attached to carbonyl carbon.
(ii) Semicarbazide has the following resonance structures arising due to the electron withdrawing nature of the O atom.
Question. The reaction of carbonyl compound with pure HCN is very slow and becomes fast in presence of a base.
Answer.With pure HCN reaction occurs very slowly because it is a weak nucleophile. With base it produces CN– ion which is a strong nucleophile and readily adds to the carbonyl compound.
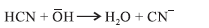
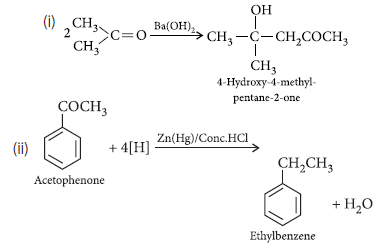
Question. Write chemical equations for the following reactions :
(i) Propanone is treated with dilute Ba(OH)2.
(ii) Acetophenone is treated with Zn(Hg)/Conc. HCl
Answer.
Question. Account for the following :
(a) Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel–Crafts reaction.
(b) pKa value of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is lower than that of benzoic acid.
Answer.(a) Due to presence of electron withdrawing group (— COOH) in aromatic carboxylic acids, they do not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(b) Due to presence of strong electron withdrawing group (—NO2), 4-nitrobenzoic acid is more acidic than benzoic acid and therefore, pKa value is lower.
Question. Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
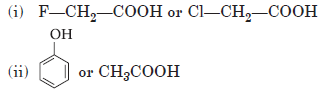
Answer.
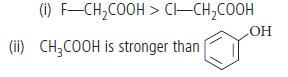
Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
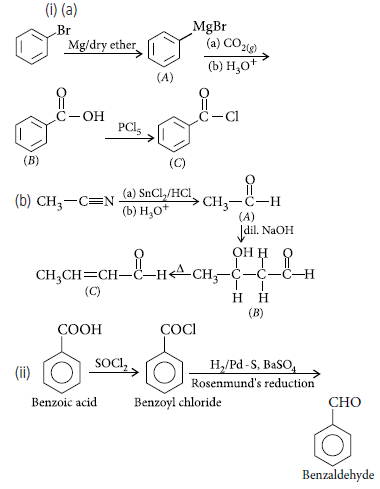
Question. (i) Write the structures of compounds A, B and C in each of the following reactions :

(ii) Do the following conversion in not more than two steps :
Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
Answer.
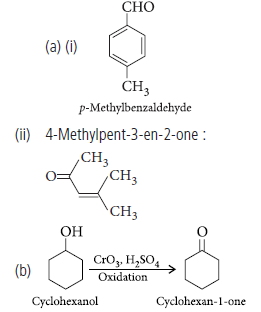
Question. (a) Draw the structures of the following :
(i) p-Methylbenzaldehyde
(ii) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
(b) Describe how the following conversions can be brought about :
Cyclohexanol to cyclohexan 1-one
Answer.
Question. During practical exams, lab assistant
provided two test tubes containing 5 mL benzoic acid and 5 mL acetaldehyde to every student. A student, Rahul found that test tubes given to him were unlabelled. He informed the teacher before performing any experiment with the given chemicals.
How can the chemicals be distinguished for correct labelling?
Answer. Chemicals can be distinguished by sodium bicarbonate test and iodoform test.
Benzoic acid will give brisk effervescence due to evolution of carbon dioxide gas with sodium bicarbonate solution while acetaldehyde does not.
Acetaldehyde will give yellow precipitate of iodoform with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution while benzoic acid does not.
Question. (i)How will you bring about the following conversions?
(a) Ethanal to but-2-enal
(b) Propanone to propene
(ii) Write the IUPAC name of the compound :
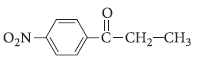
Answer.
Question. (i) Write the equations involved in the following reactions :
(a) Stephen reaction
(b) Etard reaction
(ii) Distinguish between CH3COOH and HCOOH.
Answer.
(i) (a) Stephen reduction :

(ii) Add Tollens’ reagent to formic acid and warm. Silver mirror is formed.

Acetic acid does not give this test.
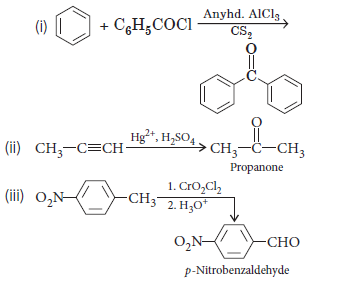
Question. Write the structures of the main products of the following reactions :
Answer.
Question. Write the equation of the reactions of ethanal with
(i) Fehling’s solution
(ii) Phenylhydrazine
(iii) Hydroxylamine.
Answer.
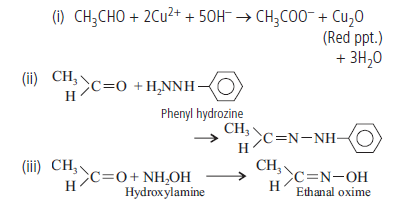
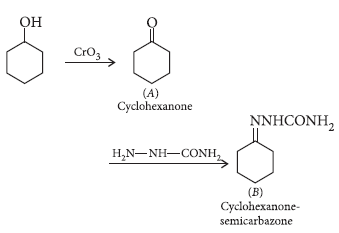
Question. (a) Write the chemical reaction involved in Wolff-Kishner reduction.
(b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction.
C6H5COCH3, CH3 CHO, CH3COCH3
(c) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and I2, isomer B forms yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate.Write the formulae of A and B.
Answer.
(a) Wolff-Kishner reduction : The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is reduced to CH2 group on treatment with hydrazine followed by heating with potassium hydroxide in a high boiling solvent such as ethylene glycol.

(b) Increasing order of reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction :
C6H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO
(c) Formula of compounds A and B is C3H6O. B forms yellow precipitate of iodoform. Hence, B must contain —COCH3 group. Therefore, compound ‘B’ must be
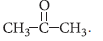
A does not give iodoform test and it is functional isomer of B thus, it may be CH3CH2CHO.
Question. In an industry aldehydes are being prepared by controlled oxidation of primary alcohol using acidified K2Cr2O7 or aqueous or alkaline KMnO4 as oxidant. Mohan suggested the owner of factory to use Collin’s reagent instead of acidic potassium dichromate. The yield of factory increased sharply.
Now answer the following questions :
(i) What is Collin’s reagent?
(ii) What are the advantages of using Collin’s reagent over conventional oxidising agent?
Answer.(i) Collin’s reagent is a mixture of pyridine (C5H5N) and CrO3 in dichloromethane (CH2Cl2).
(ii) Collin’s reagent is a mild oxidant. It oxidises 1°-alcohols to aldehydes and 2°-alcohols are oxidised to ketones.
In case of using acidic K2Cr2O7 as oxidant, the aldehydes and ketones formed by the oxidation of alcohols undergo oxidation to give carboxylic acids.
Question. (A), (B) and (C) are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C4H8O. Isomers (A) and (C) give positive Tollens’ test whereas isomer (B) does not give Tollens’ test but gives positive iodoform test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCl give the same product (D).
(a) Write the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D).
(b) Out of (A), (B) and (C) isomers, which one is least reactive towards addition of HCN?
Answer.
(a) As (A) and (C) give positive Tollens’ test thus these two should be aldehyde while (B) should be a ketone (does not give Tollens’ test) with

group (as it gives positve iodoform test).
Three isomers are

(b) out of (A), (B) and (C) isomers, (B) is least reactive towards addition of HCN.
Question. Write the products formed when ethanal reacts with the following reagents :
(i) CH3MgBr and then H3O+
(ii) Zn-Hg/conc. HCl
(iii) C6H5CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
Answer.
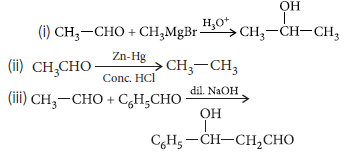
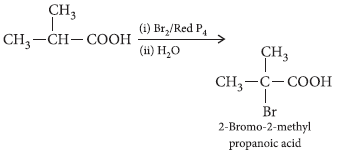
Question. Illustrate the following name reactions giving a chemical equations in each case :
(i) Clemmensen reaction
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction
Answer.(a)(i) Clemmensen reduction : The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is reduced to CH2 group on treatment with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
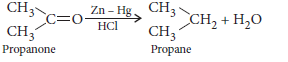
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction : Aldehydes which do not contain a-H atom undergo disproportionation when heated with concentrated (50%) NaOH.
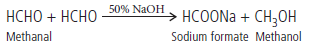
Question. Two moles of organic compound ‘A’ on treatment with a strong base gives two compound ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ on dehydrogenation with Cu gives ‘A’ while acidification of ‘C’ yields carboxylic acid ‘D’ with molecular formula of CH2O2. Identify the compounds A, B, C and D and write all chemical reactions involved.
Answer. Since the molecular formula of D is CH2O2, thus, D is HCOOH (formic acid). D is obtained by the acidification of C,so, C is sodium formate (HCOONa).
Thus, A must be formaldehyde (as it undergoes Cannizzaro reaction with a strong base).
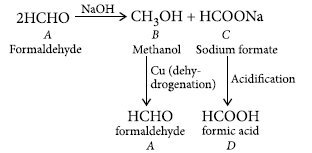
Thus, A = Formaldehyde (HCHO)
B = Methanol (CH3OH)
C = Sodium formate (HCOONa)
D = Formic acid (HCOOH)
Question. Identify A and E in the following series of reactions :

Answer.

Question. (a) Write the main product in the following equations :

(b) Write the product in the following reaction :

Answer.

Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Identify A, B and C in the following sequence of reactions :
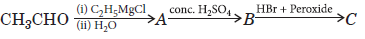
(b) Predict the structures of the products formed when benzaldehyde is treated with
(i) conc. NaOH
(ii) HNO3/H2SO4 (at 273– 383 K)
Answer.
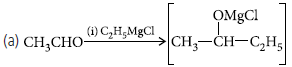
Question. (a) Give a plausible explanation for each one of the following :
(i) There are two –NH2 groups in semicarbazide.
However, only one such group is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
(ii) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2,4,6-trimethylcyclo-hexanone does not.
(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2,4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollens’ reagent and undergoes
Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation it gives 1,2-benzene-dicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
Answer.(a) (i) Semicarbazide has the following resonance structures arising due to the electron withdrawing nature of the O atom.

Lone pairs of N-1 and N-2 are involved in conjugation with
group while that of N-3 is not involved in resonance thus, it is involved in the formation of semicarbazone.
(ii) Formation of cyanohydrin involves the nucleophilic attack of cyanide ions (CN–) at the carbonyl carbon. In cyclohexanone, reaction proceeds but in 2,4,6-trimethylcyclohexanone, the methyl groups cause steric hindrance and yields are poor.
(b) The compound forms 2,4-DNP derivative. It shows that it is a carbonyl compound. Further it reduces Tollens’ reagent which shows that it contains aldehydic group. It undergoes Cannizzaro reaction indicating that aldehyde group is without any a-hydrogen. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid which shows that there are two carbon residues on benzene ring. Since the molecular formula is C9H10O, it fits into the structure, 2-ethylbenzaldehyde.

Question. An organic compound (A) on treatment with ethyl alcohol gives a carboxylic acid (B) and compound (C). Hydrolysis of (C) under acidified conditions gives (B) and (D). Oxidation of (D)
with KMnO4 also gives (B). (B) on heating with Ca(OH)2 gives (E) having molecular formula C3H6O. (E) does not give Tollen’s test and does not reduce Fehling’s solution but forms a 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazone. Identify (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E).
Answer.

Question. Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions :
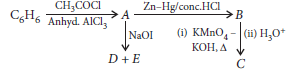
Answer.

Question. Identify A to E in the following reactions :
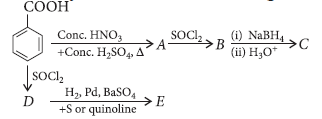
Answer.