Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set B
Please refer to Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set B with solutions provided below. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry as per the latest paper pattern and examination guidelines for Standard 12 Chemistry issued by CBSE for the current academic year. The below provided Sample Guess paper will help you to practice and understand what type of questions can be expected in the Class 12 Chemistry exam.
CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry for Set B
Topic-1
Adsorption and its Types, Factors Affecting Adsorption
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Extent of physisorption of a gas increases with
(a) increase in temperature.
(b) decrease in temperature.
(c) decrease in surface area of adsorbent.
(d) decrease in strength of van der Waals forces.
Answer
B
Question. In physisorption, adsorbent does not show specificity for any particular gas because :
(a) involved van der Waals forces are universal.
(b) gases involved behave like ideal gases.
(c) enthalpy of adsorption is low.
(d) it is a reversible process.
Answer
A
Question. The term ‘sorption’ stands for
(a) absorption.
(b) adsorption.
(c) both absorption and adsorption.
(d) desorption.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is an example of absorption?
(a) Water on silica gel
(b) Water on calcium chloride
(c) Hydrogen on finely divided nickel
(d) Oxygen on metal surface
Answer
B
B. Answer the following:
Question. Write one similarity between Physisorption and Chemisorption.
Answer. Both are surface phenomenon/both increase with increase in surface area (or any other correct similarity).
Question. Why is adsorption always exothermic ?
Answer. Due to the bond formation between the adsorbent and the adsorbate.
Question. Define Adsorption giving an example.
Answer. Adsorption is a surface phenomenon in which a substance gets accumulated on the surface of the solid rather than in the bulk of a solid or liquid.
The surface that adsorbs is called adsorbent and the one that gets absorbed a called an adsorbate. For example, air becomes dry in the presence of silica gel
Question. Out of NH3 and CO2, which gas will be absorbed more readily on the surface of activated charcoal and why ?
Answer. NH3 will be absorbed more readily on the surface of charcoal because it has higher critical temperature due to van der Waals forces of attraction.
Question. Out of physisorption or chemisorption, which has higher enthalpy of adsorption ?
Answer. Chemisorption has higher enthalpy of adsorption i.e., 80-240 kJ mol–1 as it involves chemical bond formation.
Question. Write two applications of adsorption.
Answer. The two applications of adsorption are :
(i) Activated charcoal is used in gas masks to remove poisonous gases such as carbon monoxide, methane etc. Animal charcoal is used to remove colouring matter from sugarcane juice in the manufacture of sugar.
(ii) Ion exchange resin is used to remove hardness of water.
Question. What is the effect of temperature on chemisorption ?
Answer. It first increases (as heat supplied acts as activation energy) then decreases or graphical representation.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why are powdered substances more effective adsorbents than their crystalline forms?
Answer. Powdered substances are more effective adsorbents than their crystalline forms because when a substance is powdered, its surface area increases and physisorption is directly proportional to the surface area of the adsorbent.
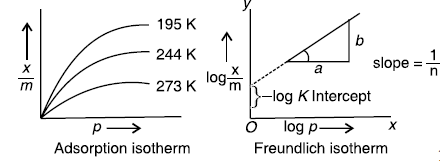
Question. What is an adsorption isotherm ? Describe Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
Answer. A graph drawn between extent of adsorption and the pressure of the gas at constant temperature is called adsorption isotherm.
A relationship between the amount adsorbed (x/m) and the equilibrium pressure (p) can be given by
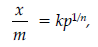
where, n is a positive integer and k is the constant.
This is known as Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
Question. Give an example where physisorption changes to chemisorption with rise in temperature. Explain the reason for change.
Answer. The process of physisorption for example that of H (hydrogen) on finely divided nickel, involves weak van der Waals forces. With increase in temperature, hydrogen molecules dissociate into hydrogen atoms which are held on the surface by chemisorption.
Long Answer Type Question-I
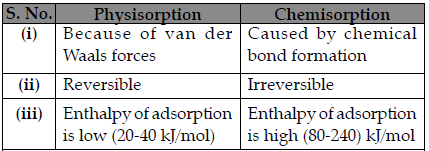
Question. Write three distinctive features of chemisorption,which are not found in physisorption.
OR
Write any three differences between Physisorption and Chemisorption.
OR
Write three differences between Physisorption and Chemisorption.
Answer.
Topic-2
Catalysis and its Types, Enzyme Catalysis
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Which of the following process does not occur at the interface of phases?
(a) Crystallisation
(b) Heterogeneous catalysis
(c) Homogeneous catalysis
(d) Corrosion
Answer
C
Question. In which of the following reactions, heterogeneous catalysts is involved ?

(a) (b), (c)
(b) (b), (c), (d)
(c) (a), (b), (c)
(d) (d)
Answer
D
B. Answer the following:
Question. What is meant by ‘shape selective’ catalysis ?
Answer. Shape selective catalysis is a chemical reaction in which the rate depends on the pore size of the catalyst, and also on the shape and size of the reactant and product molecules. Zeolite acts as shape selective catalyst.
Question. What is the role of desorption in the process of catalysis?
Answer. To make the surface available again for more reaction to occur/To remove the product formed from the surface of the catalyst.
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. How does a solid catalyst enhance the rate of combination of gaseous molecules? How does a solid catalyst enhance the rate of combination of gaseous molecules?
Answer. When gaseous molecules come in contact with the surface of a solid catalyst, a weak chemical combination takes place between the surface of the catalyst and the gaseous molecules, which increase the concentration of reactants on the surface. Different molecules adsorbed have better chance to react and form new molecules. This enhances the rate of reaction. Adsorption is an exothermic process. The heat released in the process of adsorption is utilised in enhancing the reaction rate.
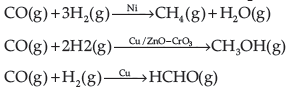
Question. What do you mean by activity and selectivity of catalysts?
Answer. Activity of a catalyst : The activity of a catalyst is to increase the rate of a particular reaction. Chemisorption is the main factor which decides the activity of a catalyst. The adsorption of reactants on the catalyst surface should be neither too strong nor too weak. It should just be strong enough to make the catalyst active.
Selectivity of the catalyst : The ability of the catalyst to direct a reaction to yield a particular product is called as the selectivity of the catalyst. For example, by using different catalysts, we can get different products for the reaction between H2 and CO.
Topic-3
Colloids, Types of Colloids, Characteristics and Preparation of Colloids
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions (1 mark each)
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Which of the following process is responsible for the formation of delta at a place where rivers meet the sea?
(a) Emulsification
(b) Colloid formation
(c) Coagulation
(d) Peptization
Answer
C
Question. At high concentration of soap in water, soap behaves as :
(a) molecular colloid
(b) associated colloid
(c) macromolecular colloid
(d) lyophilic colloid
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following will show Tyndall effect?
(a) Aqueous solution of soap below critical micelle concentration.
(b) Aqueous solution of soap above critical micelle concentration.
(c) Aqueous solution of sodium chloride.
(d) Aqueous solution of sugar.
Answer
B
Question. Method by which lyophobic sol can be protected
(a) by addition of oppositely charged sol.
(b) by addition of an electrolyte.
(c) by addition of lyophilic sol.
(d) by boiling.
Answer
C
Question. Freshly prepared precipitate sometimes gets converted to colloidal solution by
(a) coagulation.
(b) electrolysis.
(c) diffusion.
(d) peptization.
Answer
D
Question. A colloidal system having a solid substance as a dispersed phase and a liquid as a dispersion medium is classified as .
(a) solid sol.
(b) gel.
(c) emulsion.
(d) sol.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following electrolytes will have maximum coagulating value for AgI/Ag+ sol?
(a) Na2S
(b) Na3PO4
(c) Na2SO4
(d) NaCl
Answer
B
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the items given in Column I and Column II.

Answer. (i) → (b)
(ii) → (c)
(iii) → (d)
(iv) → (a)
C. Answer the following:
Question. What type of colloid is formed when a solid is dispersed in a liquid ? Give an example.
Answer. example –paints, cell fluids
Question. What type of colloid is formed when a liquid is dispersed in a solid ? Given an example.
Answer. Gel eg. cheese, butter, jellies (any one).
Question. What are emulsions ? Give one example.
Answer. Liquid –Liquid colloidal systems: example–milk
Question. What is electrophoresis ?
Answer. The movement of colloidal particles towards a particular electrode under the influence of an electric field is called electrophoresis.
Question. What type of colloid is formed when a gas is dispersed in a liquid ? Give an example.
Answer. Foam; e.g. froth, whipped cream, soap lather
Question. Write the dispersion medium and dispersed phase in milk.
OR
What are the dispersed phase and dispersion medium in milk ?
Answer. Dispersion medium – Liquid/water; Dispersed phase –Liquid /oil.
Question. What are Associated Colloids ? Give an example.
Answer. Associated colloids are the colloids which act as electrolyte at low concentration and show colloidal behaviour at high concentration. Example : Soap solution.
Question. Give one example each of ‘oil in water’ and ‘water in oil’ emulsion.
Answer. Oil in water : Milk/vanishing cream.
Water in oil : Butter/cold cream.
Question. Give one example each of sol and gel.
Answer. Sol : Paint/cell fluids.
Gel : Cheese/butter/jellies (or any other, any one example of each).
Question. A delta is formed at the meeting point of sea water and river water. Why ?
Answer. Due to coagulation of colloidal clay particles by electrolytes present in the sea.
Question. Write the dispersed phase and dispersion medium in butter.
Answer. Dispersed phase–liquid /water ; Dispersed medium -liquid/oil.
Question. To which colloidal system does milk belong ?
Answer. Milk belong to oil in water type emulsion, where dispersed phase is oil and dispersion medium is water.
Question. How can a colloidal solution and true solution of the same colour be distinguished from each other ?
Answer. When a beam of light is passed through true solution and colloidal solution kept in glass vessel, then only colloidal solution exhibits Tyndall effect whereas true solution does not. Through visibility of the solution, true solution is transparent while colloidal solution is blue.
Question. What is meant by the term peptization ?
Answer. Peptization may be defined as the process of converting a precipitate into colloidal form by shaking it with dispersion medium in the presence of small amount of electrolyte.
Question. Out of BaCl2 and KCl, which one is more effective in causing coagulation of a negatively charged colloidal Sol ? Give reason.
Answer. The coagulation power increases with increase in charge on the ions used for coagulation. Thus,BaCl2 is more effective in causing coagulation.
Ba++ > K+
Question. Why is Tyndall effect shown by colloidal solutions ?
Answer. Colloidal solutions show Tyndall effect due to the large size of colloidal particles.
Question. Which of the following is most effective in coagulating negatively charged hydrated ferric oxide sol?
(i) NaNO3
(ii) MgSO4
(iii) AlCl3
Answer. AlCl3/Al3+.
Question. Which of the following is most effective in coagulating positively charged hydrated ferric oxide sol?
(i) NaNO3 (ii) Na2SO4 (iii) (NH4)3PO4
Answer. (NH4)3PO4/PO43-.
Question. How is Brownian movement responsible for the stability of sols?
Answer. The Brownian movement has a stirring effect,which does not allow the particles to settle.
Question. Which of the following is most effective electrolyte in the coagulation of AgI/Ag+ Sol. ?
K2SO4, MgCl2, K4[Fe(CN)6].
Answer. K4[Fe(CN)6]. Greater the valence of the flocculating ion, greater is its ability to bring coagulation as per Hardy-Schulze rule. Thus, K4[Fe(CN)6] is most effective in coagulating AgI/Ag+.
Question. Where does the water present in the egg go after boiling the egg ?
Answer. When an egg is boiled, the proteins present inside the egg gets denatured and coagulate. After boiling the egg, the water present in it is absorbed by the coagulated protein through H-bonding.
Question. Based on the type of dispersed phase, what type of colloids are dispersed phase?
Answer. Associated Colloids
Question. Write the main reason for the stability of colloidal sols.
Answer. The stability for colloidal sols is due to Brownian movement and presence of equal and similar charges which causes repulsion between them and prevents the coagulation of the sol.
Question. Give one example each of lyophobic sol and lyophilic sol.
Answer. Lyophilic sol : Metal sol, metal sulphides/hydroxides (or any other, any one example in each case).
Lyophobic sol : Gum/gelatin/starch/rubber.
Question. Out of NH3 and CO2, which gas will be adsorbed more readily on the surface of activated charcoal and why ?
Answer. NH3 will be adsorbed more readily on the surface of charcoal because it has higher critical temperature due to van der Waals forces of attraction.
Question. In reference to surface chemistry, define dialysis.
Answer. Dialysis : Dialysis is a process of removing a dissolve substance from a colloidal solution by means of diffusion through a suitable membrane
Question. How is a sol different from an emulsion?
Answer. In sol, the dispersed phase is solid and dispersion
medium is liquid.
Example : Paint
In emulsion, the dispersed phase is liquid and dispersion medium is also liquid.
Example : Milk.
Question. Which of the following is most effective in coagulating positively charged methylene blue sol?
(i) Na3PO4 (ii) K4 [Fe(CN)6] (iii) Na2SO4
Answer. K4[Fe(CN)6]/[Fe(CN)6]4-.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain the following :
(i) Same substance can act both as colloids and crystalloids.
(ii) Artificial rain is caused by spraying salt over clouds.
Answer. (i) The nature of the substance whether colloid or crystalloid depends upon size of the solute particles.
When the size of solute particles lies between 1 to 1000 nm, it behaves as a colloid.
(ii) The colloidal water particles of the clouds get neutralized and coagulated to bigger water drops by spraying salt over clouds and as a result artificial rain is caused.
Question. Do the vital functions of the body such as digestion get affected during fever? Explain your answer.
Answer. The rate of an enzyme reaction is maximum at a particular temperature range, called optimum temperature. On either side of the optimum temperature, the enzyme activity decreases. The optimum temperature range for enzymatic activity is 298–310 K. Normal human body temperature being 310 K is suited for enzyme-catalysed reactions. If a person is suffering from fever, the temperature will be over 310 K. This will adversely affect the enzymatic reactions.
Question. How are the following colloidal solutions prepared ?
(i) Sulphur in water,
(ii) Gold in water.
Answer. (i) A colloidal solution of sulphur can be obtained by passing hydrogen sulphide gas into a solution of sulphur dioxide in water.
SO2 + 2H2S → 3S + 2H2O
(ii) A colloidal solution of gold in water can be prepared by reducing auric chloride with stannous chloride.
2AuCl3 + 3SnCl2 → 2Au + 3SnCl4
Question. How does the precipitation of colloidal smoke take place in Cottrell precipitator?
Answer. In Cottrell precipitator, charged smoke particles are passed through a chamber containing plates with charge opposite to the smoke particles. Smoke particles lose their charge on the plates and get precipitated.
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. (i) Differentiate between adsorption and absorption.
(ii) Out of MgCl2 and AlCl3, which one is more effective in causing coagulation of negatively charged sol and why ?
(iii) Out of sulphur sol and proteins, which one forms multimolecular colloids ?
Answer.

(ii) AlCl3 is more effective in causing coagulation of negatively charged sol because according to Hardy and Schulze rule greater the valency of the flocculating ion, greater is its ability to bring coagulation.
(iii) Sulphur sol forms multimolecular colloids
Question. Write one difference in each of the following :
(i) Multimolecular colloid and Associated colloid
(ii) Coagulation and Peptization
(iii) Homogeneous catalysis and Heterogeneous catalysis
OR
(i) Write the dispersed phase and dispersion medium of milk.
(ii) Write one similarity between physisorption and chemisorption.
(iii) Write the chemical method by which Fe(OH)3 sol is prepared from FeCl3.
Answer.
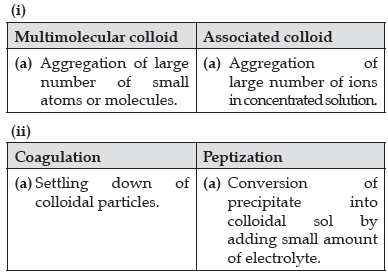

OR
(i) Dispersed phase – liquid, Dispersion medium – liquid
(ii) Both are surface phenomenon / both increase with increase in surface area (or any other correct similarity)
(iii) Hydrolysis/

Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Lyophilic colloid,
(ii) Zeta potential,
(iii) Associated colloids.
Answer. (i) Lyophilic colloid : Liquid loving colloidal sols directly formed by mixing substances like gum,gelatine, starch, rubber, etc., with a suitable liquid
(the dispersion medium) are called lyophilic sols.e.g., muddy water.
(ii) Zeta potential : The potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opposite charges is called the electrokinetic potential or zeta potential.
(iii) Associated colloids : There are some substances which at low concentrations behave as normal strong electrolytes, but at higher concentrations exhibit colloidal behaviour due to the formation of aggregates. The aggregated particles thus formed are called associated colloids or micelles.
Question. Write one difference in each of the following:
(i) Lyophobic sol and Lyophilic sol
(ii) Solution and Colloid
(iii) Homogeneous catalysis and Heterogeneous catalysis
Answer. (i) Lyophobic are liquid(dispersion medium)- hating and lyophillic are liquid (dispersion medium)-loving colloids.
(ii) Solution is a Homogeneous mixture while colloid is heterogeneous mixture /does not show tyndall effect – shows tyndall effect.
(iii) Homogeneous catalysis: reactant and catalyst are in same phase – Heterogeneous catalysis: reactant and catalyst are not in same phase.
Question. Define the following terms with an example in each:
(i) Lyophobic colloids
(ii) Homogeneous catalysis
(iii) O/W emulsion
Answer. (i) The particles of the dispersed phase have no affinity for the dispersion medium / solvent repelling (hating) colloidal sols.
Example, metal and their sulphides.
(ii) The reactant and the catalyst are in the same phase.

(iii) Oil is dispersed in water /oil is dispersed phase and water is dispersion medium. Ex-milk
Question. Explain the following phenomenon giving reasons:
(i) Tyndall effect
(ii) Brownian movement
(iii) Physical adsorption decreases with increase in temperature.
Answer. (i) The colloidal particles scatter light in all direction in space.
(ii) The zig-zag movement of particles of the dispersed phase due to unbalanced bombardment of the colloidal particles by the molecules of dispersion medium.
(iii) As the adsorption is an exothermic process, it decreases with increase in temperature.
Question. Write one difference between each of the following :
(i) Multimolecular colloid and Macromolecular colloid
(ii) Sol and Gel
(iii) O/W emulsion and W/O emulsion
Answer. (i) Multimolecular colloid : A large number of atoms or smaller molecules of a substance aggregate together to form species having size in the colloidal range.
Macromolecular : A large sized molecules whose particle size lies in the colloidal range .
(ii) Sol are solid dispersed in liquid while gel are liquid dispersed in solid.
(iii) In O/W emulsion , water acts as dispersion medium while in W/O oil acts as dispersion medium.
Question. Explain what is observed when :
(i) A beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution.
(ii) NaCl solution is added to hydrated ferric oxide sol.
(iii) Electric current is passed through a colloidal solution.
Answer. (i) Scattering of light by the colloidal particles takes place and the path of light becomes illuminated.
This is called Tyndall effect.
(ii) The positively charged colloidal particles of hydrated ferric oxide sol get coagulated by the oppositely charged ions provided by electrolyte NaCl.
(iii) On passing direct current, the colloidal particles move towards the oppositely charged electrode where they lose their charge and get coagulated.
Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Electrophoresis,
(ii) Adsorption,
(iii) Shape-selective catalysis.
Answer. (i) Electrophoresis : The movement of colloidal particles towards oppositely charged electrode in an electric field is called electrophoresis.
(ii) Adsorption : The phenomenon of attracting and retaining the molecules of a substance on the surface of a liquid or solid leading to a higher concentration on the surface in comparison to the bulk is called adsorption.
(iii) Shape-selective catalysis : The catalytic reaction which depends upon the pore structure of the catalyst and the size of the reactant and product molecules is known as shape-selective catalysis.
Question. Explain the following phenomenon giving reasons:
(i) Chemical adsorption increases with increase in temperature.
(ii) Alum is applied on a cut to stop bleeding.
(iii) Sky appears blue in colour.
Answer. (i) High energy of activation is needed.
(ii) Blood being a colloidal solution, gets coagulated by alum (an electrolyte).
(iii) Dust particles along with water suspended in air scatter blue light which reaches our eyes.
Question. How are the two types of emulsions different from one another ? Give suitable examples to justify the difference. State two applications of emulsions.
Answer. Two types of emulsions are as follows :

Application of Emulsions :
(i) In medicine : The various pharmaceuticals and cosmetics are available in liquid form such as cod liver oil etc., and some creams and ointment are emulsions of water in oil type.
(ii) Cleaning action of soap : This action is based on the formation of oil in water type emulsions.
Question. (i) Write the expression for Freundlich’s equation to describe the behaviour of absorption from solution.
(ii) What causes charge on sol particles?
(iii) Name the promoter used in the Haber’s process for the manufacture of ammonia.
Answer.

(ii) The charge on the sol particles is due to
(a) Electron capture by sol particles during electrodispersion.
(b) Preferential adsorption of ions from solution.
(c) Formulation of electrical double layer.
(iii) Molybdenum acts as a promoter for iron.
Question. (i) How can we get the following colloidal solutions :
(a) Silver in water,
(b) Sulphur in water,
(c) Fe(OH)3 in water,
(d) Gold in water.
(ii) List two applications of adsorption.
Answer. (i) (a) Silver sol in water is prepared by striking electric arc between two silver rods suspended in alkaline water. (Bredig’s arc method)
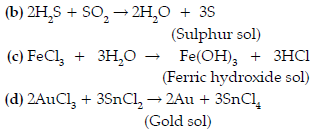
(ii) (a) The gas masks function on principle of adsorption.
(b) Chromatography is based on adsorption phenomenon.
Question. What happens when
(a) a freshly prepared precipitate of Fe(OH)3 is shaken with a small amount of FeCl3 solution ?
(b) persistent dialysis of a colloidal solution is carried out ?
(c) an emulsion is centrifuged ?
Answer. (a) Peptization occurs / Colloidal solution of Fe(OH)3 is formed
(b) Coagulation occurs
(c) Demulsification or breaks into constituent liquids
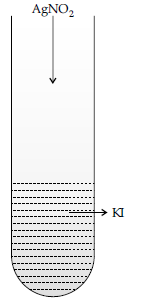
Question. (a) A colloidal sol is prepared by the given method in figure. What is the charge of AgI colloidal particles in the test tube? How is the sol formed, represented?
(b) Explain how the phenomenon of adsorption finds application in Heterogeneous catalysis.
(c) Which of the following electrolytes is the most effective for the coagulation of Fe(OH)3 sol which is a positively charged sol ?
NaCl, Na2SO4, Na3PO4
Answer. (a) Negative charge is developed on the sol.
Sol is represented as AgI /I–
(b) Adsorption of reactants on the solid surface of the catalysts increases the rate of reaction.
(c) Na3PO4
Hardy-Schulze rule
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Desorption
(ii) Critical micelle concentration
(iii) Shape selective catalysis
Answer. (i) The process of removing an adsorbed substance from a surface on which it is absorbed.
(ii) The formation of micelles takes place only above a particular concentration called CMC.
(iii) The catalytic reaction that depends upon the pore structure of the catalyst and size of the reactant and product molecules.
Question. Give a reason for the following :
(i) Rough surface of catalyst is more effective than smooth surface.
(ii) Smoke is passed through charged plates before allowing it to come out of chimneys in factories.
(iii) Ne gets easily adsorbed over charcoal than He.
Answer. (i) Rough surface of a catalyst provides more surface area for adsorption.
(ii) So that unburnt charged carbon particles get settled between the charged plate leaving behind air free from pollutants.
(iii) Ne has higher critical temperature i.e., stronger van der Waals forces therefore gets easily adsorbed.
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Kraft temperature
(ii) Peptization
(iii) Electrokinetic potential
Answer. (i) Temperature above which micelle formation takes place.
(ii) Process of converting freshly prepared precipitate into sol by shaking it with dispersion medium along with a small amount of suitable electrolyte.1
(iii) The potential difference between fixed layer and the diffused layer.
Question. Answer the following questions :
(i) What happens when a freshly precipitated Fe(OH)3 is shaken with a little amount of dilute solution of FeCl3 ?
(ii) Why are lyophilic colloidal sols more stable than lyophobic colloidal sols ?
(iii) What form Freundlich adsorption equation will take at high pressure ?
Answer. (i) A reddish brown coloured colloidal solution is obtained.
(ii) Stability of lyophilic sols is due to :
(a) same charge on all the colloidal particles.
(b) solvation of the colloidal particles.
(iii) At high pressures, amount of gas adsorbed (x/m) becomes independent of pressure (P).
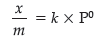
Question. Give reasons for the following observations :
(i) Leather gets hardened after tanning.
(ii) Lyophilic sol is more stable than lyophobic sol.
(iii) It is necessary to remove CO when ammonia is prepared by Haber’s process.
Answer. (i) Mutual coagulation
(ii) Strong interaction between dispersed phase and dispersion medium or solvated layer
(iii) CO acts as a poison for catalyst
Question. What are emulsions ? What are their different types ? Give one example of each type.
Answer. Emulsions are liquid-liquid colloidal systems or the dispersion of one liquid in another liquid.
Types : (i) Oil dispersed in water (O/W type)
Example ; milk and vanishing cream
(ii) Water dispersed in oil (W/O type) Example;butter and cold cream.
Question. Give reason for the following observations :
(i) When Silver nitrate solution is added to Potassium iodide solution, a negatively charged colloidal solution is formed.
(ii) Finely divided substance is more effective as an adsorbent.
(iii) Lyophilic colloids are also called reversible sols.
Answer. (i) The precipitated silver iodide adsorbs iodide ions from the dispersion medium resulting in the negatively charged colloidal solution.
(ii) Due to large surface area
(iii) If the dispersion medium is separated from the dispersed phase , the sol can be reconstituted by simply remixing with the dispersion medium.
That is why these sols are also called reversible sols.
Question. Describe the following processes :
(i) Dialysis,
(ii) Electrophoresis,
(iii) Tyndall effect.
Answer. (i) Dialysis : It is a process of removing a dissolved substance from a colloidal solution by means of diffusion through a suitable membrane.
(ii) Electrophoresis : The movement of colloidal particles towards oppositely charged electrode in an electric field.
(iii) Tyndall effect : When a strong converging beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution placed in a dark room, the path of beam gets illuminated with a bluish light when viewed at right angles to the direction of the passage of light. This phenomenon is known as Tyndall effect.
Question. (i) Adsorption of a gas on surface of solid is generally accompanied by a decrease in entropy, still it is a spontaneous process. Explain.
(ii) Some substances can act both as colloids and crystalloids. Explain.
(iii) What will be the charge on AgI colloidal particles when it is prepared by adding small amount of AgNO3 solution to KI solution in water ? What is responsible for the development of this charge ?
Answer. (i) DS = negative but DH is also negative due to attraction. DG = DH – TDS, DG can be negative if DH has sufficiently high negative value as –TDS is positive. So, in adsorption process, a combination of these two factors makes DG negative.
(ii) There are some substances which at low concentration behave as normal strong electrolytes, but at higher concentrations exhibit colloidal behaviour due to the formation of aggregates.
(iii) When silver nitrate solution is added to KI solution, the precipitated AgI adsorbs iodide ions from the dispersion medium and negatively charged colloidal solution results. Since KI is in excess,iodide ions (I–) will be adsorbed on the surface of AgI particles thereby giving them a negative charge.

Long Answer Type Question-II
Question. What is the difference between multi-molecular and macro-molecular colloids? Give one example of each. How are associated colloids different from these two types of colloids?
Answer. (i) In multi-molecular colloids, the colloidal particles are an aggregate of atoms or small molecules with a diameter of less than 1 nm. The molecules in the aggregate are held together by van der Waals forces of attraction. Examples of such colloids include gold sol and sulphur sol.
(ii) In macro-molecular colloids, the colloidal particles are large molecules having colloidal dimensions. These particles have a high molecular mass. When these particles are dissolved in a liquid, sol is obtained.
For example : Starch, nylon, cellulose, etc.
(iii) Certain substances tend to behave like normal electrolytes at lower concentrations.
However, at higher concentrations, these substances behave as colloidal solutions due to the formation of aggregated particles. Such colloids are called aggregated colloids.
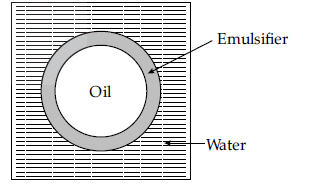
Question. How do emulsifiers stabilise emulsion? Name two emulsifiers.
Answer.(i) It is believed that an emulsifier gets concentrated at the oil-water interface i.e., the surface at which oil and water come in contact with each other. It forms a protective coating around each drop of oil and thus, prevents the oil drop from coming in contact with one another. The oil drops remain suspended in water and are not coagulated.
(ii) According to an another view, the role of the emulsifier is the same as that of lubricant in a machine. Just as a lubricant reduces the friction in the various parts of machine, an emulsifier also tries to reduce the interfacial tension between oil and water by suitable meAnswer. Thus, oil and water remain in company of each other and do not get separated. The commonly used emulsifying agents are soaps, detergents, lyophilic colloids, proteins, gums, gelatin, caesin, agar etc.
