Exam Question for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 The Theory of the Firm Under Perfect Competition
Please refer to below Exam Question for Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 The Theory of the Firm Under Perfect Competition. These questions and answers have been prepared by expert Class 12 Economics teachers based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Economics and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Economics exam questions for all chapters in your textbooks. You will be able to easily learn problems and solutions which are expected to come in the upcoming class tests and exams for standard 12th.
Chapter 4 The Theory of the Firm Under Perfect Competition Class 12 Economics Exam Question
All questions and answers provided below for Exam Question Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 The Theory of the Firm Under Perfect Competition are very important and should be revised daily.
Exam Question Class 12 Economics Chapter 4 The Theory of the Firm Under Perfect Competition
MCQs
Question. Condition for producer equilibrium is
a) TR=TVC
b) MC=MR
c) None of above
d) TC=TSC
Answer
B
Question. Under which market situation demand curve is linear and parallel to X-axis?
a) Monopoly
b) Perfect competition
c) Oligopoly
d) Monopolistic competition
Answer
B
Answer
A
Question. A competitive firm in the short run incurs losses. The firm continues production, if?
a) P>AVC
b) P=AVC
c) P>=AVC
d) P<AVC
Answer
C
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Define perfect competition
Answer : Perfect competition is a market with large number of buyers and sellers, selling homogeneous product at same price.
Question. What is oligopoly?
Answer : Oligopoly is defined as a market structure in which there are few large sellers who sell either homogenous or differentiated goods.
Question. What is the shape of marginal revenue curve under monopoly?
Answer : Under monopoly market, marginal revenue cuve is downwards sloping from left to right and it lies below the average revenue curve.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain the implication of free entry and free exit of a firm in perfect competitive market?
Answer : If there is free entry and free exit of firms, then no firm can earn abnormal profit in the long run. That is firm earn zero abnormal profit. Each firm earns just normal profit.
Q19. Which features of monopolistic competition are monopolistic in nature?
Answer : The features are as below:
1) Product Differentiation
2) Control over price
3) Downward sloping demand curve
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Distinguish between change in supply and change in quantity supplied.
State two factors responsible for change in supply.
Answer : A change in supply is a change in the relationship between price and how much suppliers make, whereas a change in quantity supply is *any* change in the amount that gets bought and sold. Difference between change in supply and change in quantity supplied occurs due to changes in factors affecting supply. When price of the commodity supplied changes then there is change in quantity supplied. There is a movement along the same supply curve. When factors other than the price of the commodity changes, for say prices of related commodities, prices of inputs, technology etc. there is a change in supply. The supply curve shifts, either left or right.
Right below is the diagram of Change in supply:

Again, the supply curve is isolated. A change in supply means a shift in the entire curve. In this case, supply has expanded because it has shifted to the right. If we had a demand curve here we would observe a higher quantity supplied at a lower equilibrium price after the shift in supply.
A change in quantity supplied would be shown on a graph as such:

Note that this is the supply curve isolated on the graph. At each point on the curve there is a different quantity supplied. So, if we change from p = 1 to p = 2, there is a change in quantity supplied of 20 units since we have gone from q = 10 at p = 1 to q = 30 at p = 2.

Factors responsible for change in supply are as follows:
1. Production costs: Input prices and resulting production costs are
inversely related to supply. In other words, changes in input prices and production costs cause an opposite change in supply. For example, if wages or labour costs increase, the supply of the good decreases.
2. Technology: Technological improvements in production shift the supply curve. Specifically, improvements in technology increase supply — a rightward shift in the supply curve.
3. Prices of other goods: Price changes for other goods are a little complicated. First, in order to affect supply, producers must think the goods are related. What consumers think is irrelevant. For example, ranchers think beef and leather are related; they both come from a steer.
Question. When a price of a commodity rises from Rs. 10 to Rs. 11 per unit, its quantity supplied rises by 100 units. Its price elasticity of supply is 2.
Calculate its quantity supplied at the increased price.
Answer :
It is given in the question that:-
P = 10, P1 = 11, thus ΔP = 11-10 = 1
Q =? ΔQ = 100 units, Es = 2
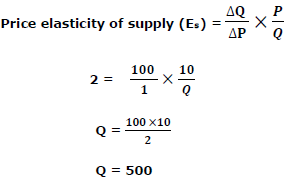
Therefore, quantity supplied at the increase price = Q+ΔQ=500+100=600
units.
